Hand Soap Liquid,Hand Foam Soap,Wash Hand Soap,Soap Hand Wash Wuxi Keni Daily Cosmetics Co.,Ltd , https://www.kenicosmetics.com
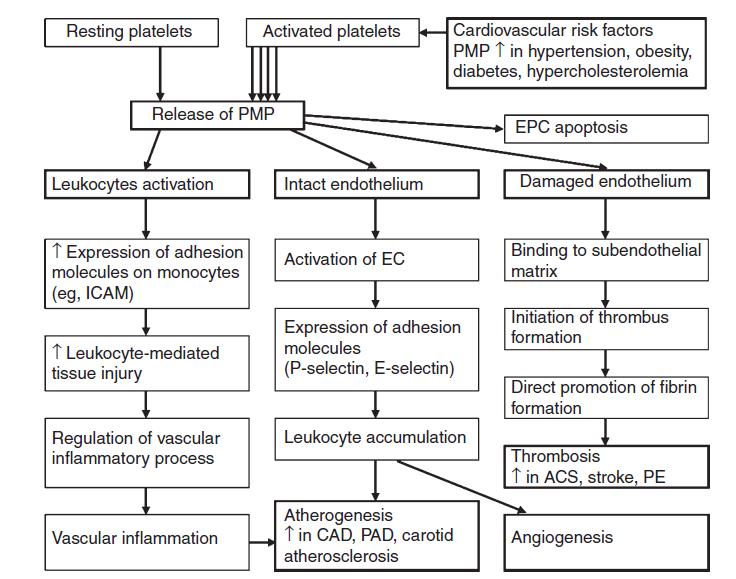
Recent studies have shown that exocrine circulating microparticles are contributing factors to cardiovascular inflammation, clogging and injury. In the past, due to the limitations of conventional equipment in the detection of tiny particles, the important factor of circulating particles was excluded from the cause analysis. The Apogee nano-scale ultra-high resolution flow cytometer introduced by Puri McGrady, with its unique 80nm scattered light resolution and sensitivity of 10nm, broke through the bottleneck of exosomes and microvesicles for the first time, leading the frontier scientific explosion! 
In response to the limitations of conventional equipment on exosomes, in February 2013, Shantsila E, Gregory YH Lip of the Centre for Cardiovascular Science at the University of Birmingham and Kamphuisen of the Department of Vascular Medicine at the University of Amsterdam published a book entitled "Circulating microparticles in Cardiovascular Disease". A review article for :implications for atherogenesis and atherothrombosis.
Just one month after exposure to Apogee nanoscale flow cells, in April 2013, the Cardiovascular Science Research Center of the University of Birmingham (Gregory YH Lip, etc.) and the Cardiovascular Hospital of Murcia-Dal Ariksaka, Spain Center, using Apogee's unique 80nm ultra-high resolution and 10nm ultra-sensitivity to detect the circulating particles studied, obtained some very valuable new data, achieved unexpected results, and the paper of the research results " Small-size circulating microparticles in acute coronary syndromes: Relevance to fibrinolytic status, reparative markers and outcomes" was successfully published in the journal Atherosclerosis. 
Conventional flow cytometry is a powerful tool that is directly used for the detection of extracellular vesicles (EV) and exocrines, but is subject to several challenging obstacles. The biggest limitation is that these vesicles are small (exocrine 80-200 nm, microvesicles 200-1000 nm), polydispersity, low refractive index; when using the lipophilic dye PKH67 and antibody labeling, even if the commercial high-end flow optimization version is used for analysis, it needs to be rich. Experiments with streaming experience and the ability to manually adjust the hardware and calibrate the instrument to complete the experiment, and the resolution of the instrument is limited, resulting in often inaccurate test results.
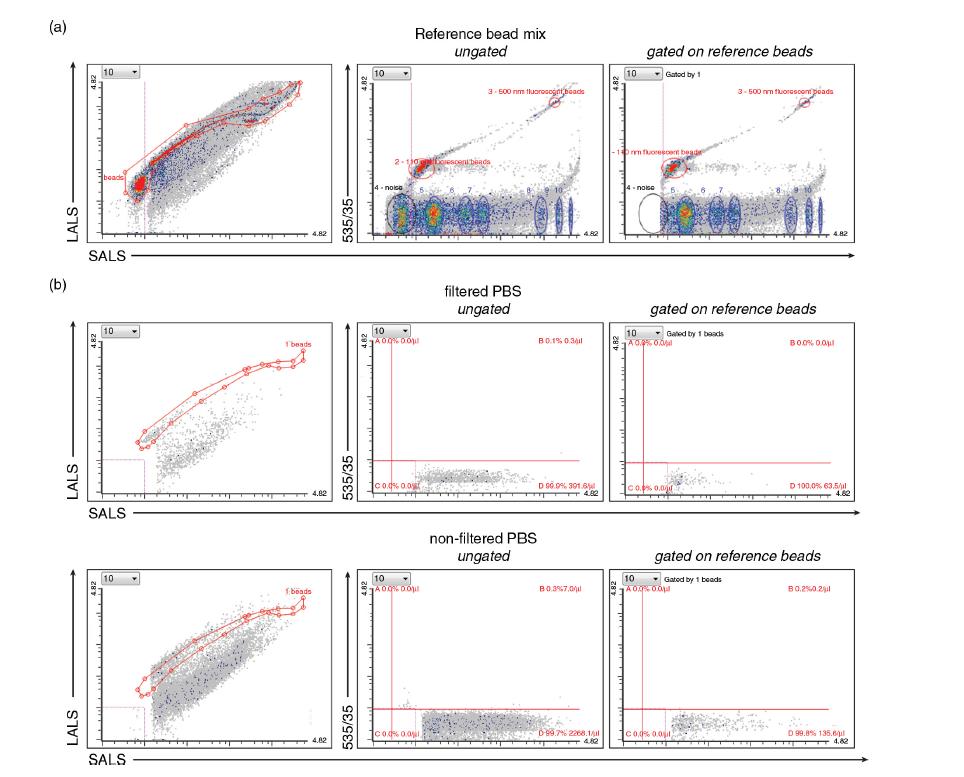
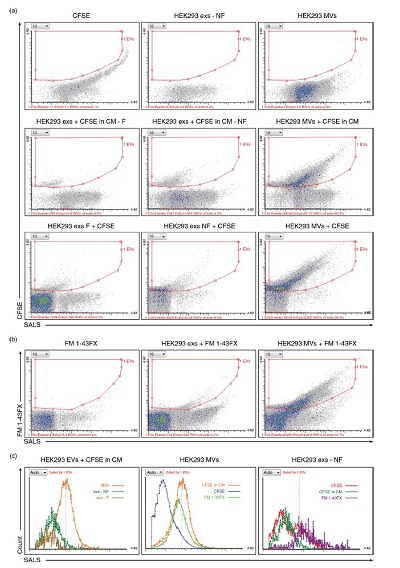
Apogee A50 nano-scale ultra-high resolution flow cytometer, due to its unique 80 nm scattered light resolution and high sensitivity of 10 nm, can separate exocrine and microcapsules from cell culture media and complex human samples. Quantification and specificity analysis of bubbles (eg ascites in patients with ovarian cancer). Designed for microparticle detection and multi-purpose assays, the EVs can be labeled with fluorescent protein (CFSE) or lipid (FM) specific dyes without data removal without conjugated fluorescence. Dyes, further accelerating the detection of microvesicles and exosomes by flow cytometry, breaking through the traditional flow cytometry detection of exosomes is limited only to the size parameters, unable to distinguish the composition of the particles (such as the total amount of protein, Microsomes, lipoprotein properties or abundance of specific proteins, etc., often lead to limitations in the overestimation of the number of extracellular vesicles. Apogee A50 provides a novel and rapid method for the study of exocrine and microvesicles.
Highlight 2: High-concentration sample (10 9 cell/mL) for direct detection, turbid liquid can also be directly loaded
Highlight 3: Wide sample detection range 10 2 -10 9 cell/mL
Highlight 4: Unique time stamp function to monitor the accuracy of experimental results at any time, give up unreasonable data
Highlight 5: Ultra-precise sample control with a minimum flow rate of 0.7 uL/min
Highlight 6: Ultra-high constant performance Fluorescence channel CV value ≤ 1.5%
Exosomes are a class of nanoscale vesicles, and almost all types of cells, including cancer cells, can release exosomes. As an important mediator of intercellular communication, exosomes mediate the exchange of proteins and genetic material. There is increasing evidence that exosomes secreted by host cells or cancer cells are involved in tumorigenesis, growth, invasion and metastasis. And immune cells and cancer cells themselves communicate through exosomes and play a dual role in regulating tumor immunity.
1. Micro-circulating particle detection----Innovative breakthrough
 Figure 1. Cardiovascular disease-related circulating particle formation and transport pathways
2, exosomes / microvesicle detection ------ high precision analysis (Journal of Extracellular Vesicles 2015, 4: 25530)
Figure 2. Small particle detection bead verification
Figure 3. Comparison of normal cell and cancerous cell exosomes. Results show high-precision exosomes / microvesicles detection rate
Apogee A50 nano-scale flow exosomes/microvesicle detection advantages showcase
Highlight 1: Unique scattering light sensitivity 80nm and resolution 10nm, 10 times higher than the traditional flow, up to 3 laser and 12 detectors, and can be equipped with an autosampler
Contact information:
Purui Maddy (Beijing) Laboratory Technology Co., Ltd.
Website:
E-mail:
Free hotline
phone
fax