Release date: 2010-10-08 Source: Frontier Medical Information Network
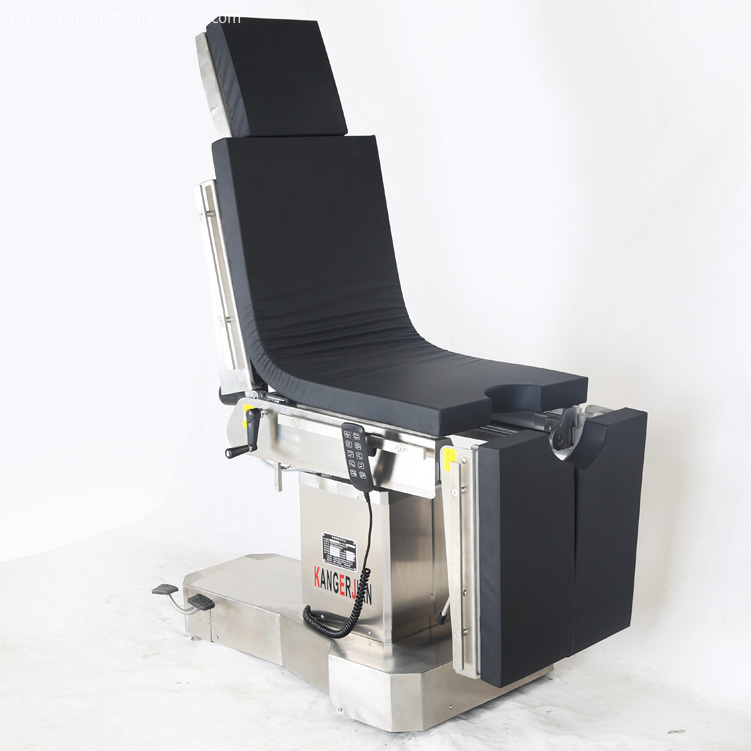
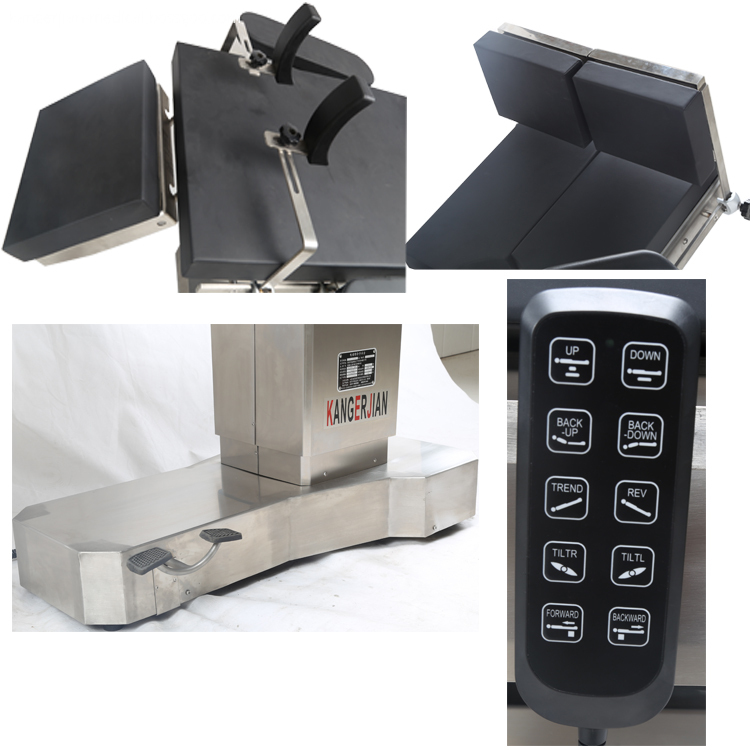
Electric power source Operating Table , selection of Motor push rod power, high quality and reliability. Electric Surgical Table, 2. Use imported gas spring as the manual power source of the operating table, stable performance. Electric OT Table, 3. Operating table using medical-grade 304 stainless steel, more modern, cleaner and more convenient. Integrated operating table, Electric Surgery Table, 4. High-strength stainless steel bottom cover, compressive ability, anti-corrosion, easy to clean. 5 head and leg plate removable, easy to operate, provide more flexible surgical space. Electric Operation Table, 6. Hand control, and has a key switch to prevent misuse. 7. Operating table base has a fixed or mobile function, mobile and flexible, fixed and reliable. 8. Countertop optional built-in waist bridge, gallbladder, kidney and other operations to provide convenience. Hospital integrated operating table, 9. Optional built-in battery to protect the operating table without interruption. 10. Table optional longitudinal translation, to achieve all-C shooting.
Electric Operating Table,Electric Hospital Beds,Electric Medical Operating Table,Medical Electric Operating Table Shandong Kang'erjian Medical Technology Ltd. , https://www.operatingtable.nl
According to a new Canadian study published in the October 12 issue of Circulation, a new Internet-based tool can more accurately predict the risk of death in hospitals for stroke patients and help doctors develop better Care plan.
Doctors can also use predictive tools to assess and improve patient clinical outcomes, said Dr. Eric Smith, author of the study, and assistant professor of neurology at the University of Calgary, Alberta, Canada.
The tool is called the Get With The Guidelines-Stroke (GWTG) predictive tool, which is based on a large number of stroke patient samples across the country. The doctor uploads the patient's admission information and predicts the risk of death by computer calculation based on factors such as age, gender, and other diseases.
“Hospitals can use our death risk scores to calculate the expected mortality rates based on their own characteristics and compare them to the actual observed mortality,†Smith said. “This may help improve the quality of care.â€
The study analyzed medical records and demographic data for nearly 275,000 stroke patients from 2001 to 2007 and developed a range of mortality predictions based on their clinical outcomes. The data comes from hospitals participating in the American Heart Association's Get With The Guidelines program.