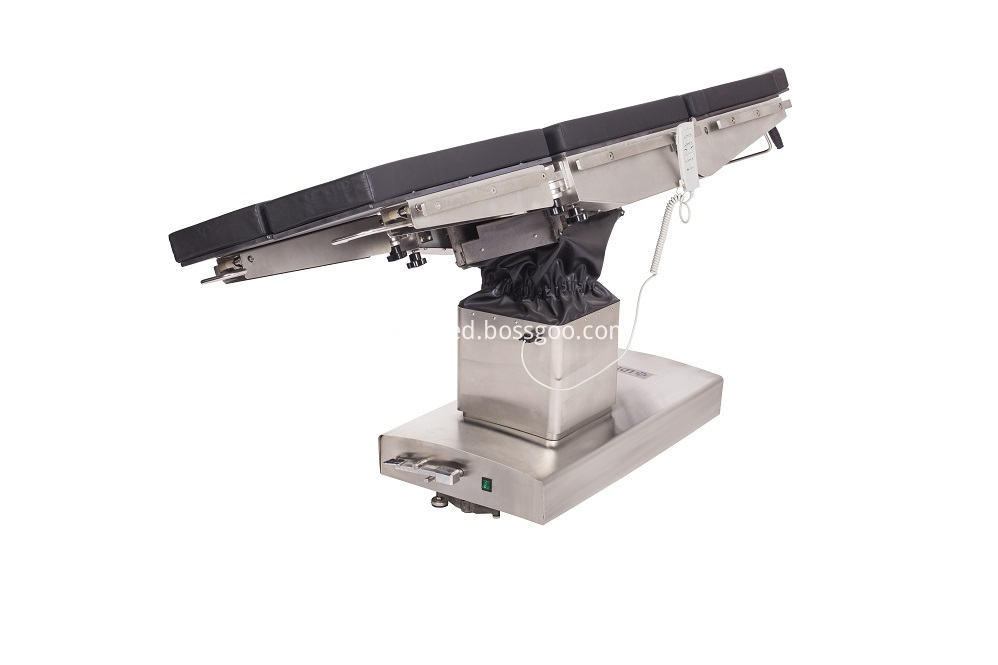
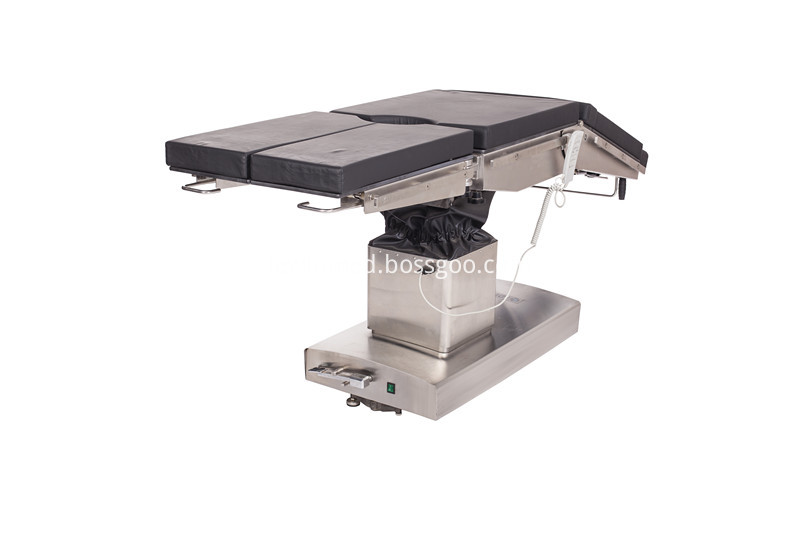
Electric Operating Table Adopt imported TIMOTION electric push rod as the power source for the operation tables. Adopt German imported STABILUS as the power source of the operation beds; Operation beds adopt medical grade 304# full stainless steel materials; Full set of micro electric control system for ot table with low noise, overload protection, safty reliablity; TheElectric Operating Table entire table of operating table can move forward and backward to realize full position C-arm and X-ray radiography;
Electric Operating Table Electric Operation Table,Electric OT Table,Electric Surgery Table,Electric Surgical Table Shandong Lewin Medical Equipment Co., Ltd. , https://www.operatinglight.nl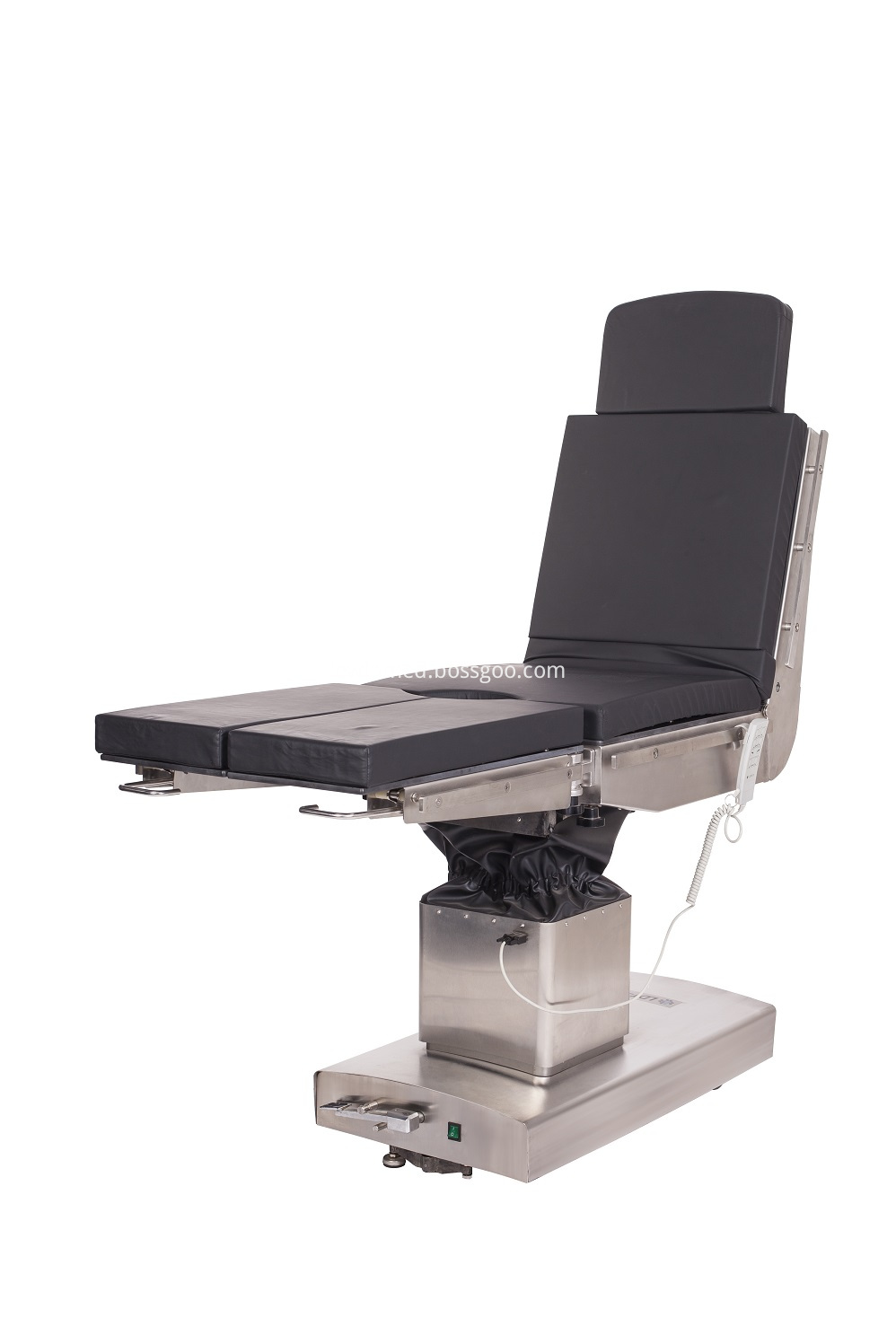


1. Characteristics of required fertilizer for Chinese St. Peach The Chinese St. Peach has a large fruit size, luxuriant foliage, and rapid growth. It has a high demand for nutrient elements and is sensitive to reactions. In order to meet the demand for various elements in the growth and results of Chinese sacred peach, only through soil analysis and leaf analysis results, reasonable fertilization can timely supplement the deficiency of nutrient elements. Chinese Sheng Tao needs a variety of nutrients in its lifetime, which requires the largest number of NPK. Chinese Peach is sensitive to nitrogen and requires a high nitrogen content. The maximum amount of absorbed nitrogen is the leaf, which accounts for nearly half of the total nitrogen requirement. Undoubtedly, sufficient supply of nitrogen is the basis for the high yield of Chinese Peach. Its absorption of phosphorus is also relatively high, which leaves more absorption. In the three elements of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, the absorption of potassium is the highest, which is 1.6 times that of nitrogen, especially the absorption of fruit is the largest. Therefore, meeting the need of potassium in time is the key to high yield and high quality of peach. According to the determination, the ratio of the total absorption of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in Chinese cherry tree is 10:3 to 4:13 to 16. Second, the major nutrients and nutrient deficiency symptoms required for Chinese St. Peach (1) Nitrogen and Chinese St. Peach are more sensitive to nitrogen. Insufficient, shoot growth is short, thin leaves, light color. Severe nitrogen deficiency, green and yellow leaves, red and brown spots on the base leaves, perforation; branches short, slender; fruit small, astringent, poor quality; low yield, short tree life. When there is too much nitrogen, the branches and leaves grow too prosperous, the canopy closes, there are few flower buds, the fruit setting rate is low, the fruit is small, the taste quality is poor, the coloring is not good, and the disease is susceptible. (b) Phosphorus and phosphorus levels are related to photosynthesis, respiration and metabolism and operation of carbohydrates and nitrogen compounds. Phosphorus can operate in the peach tree and is an important element in flower bud formation. Phosphorus deficiency was similar to that of nitrogen deficiency in Chinese Peach. Symptoms mostly occurred on new shoots and old leaves. The leaves were small and dark green or brown in color. When the leaves were cold, they turned red or purple, and the parietal leaves were upright. The development of fine roots is blocked, the plants are dwarfed, the fruit is ripe, the juice is less, the flavor is poor, and there are deep longitudinal cracks and fluidity. (3) Potassium Potassium plays an important role in the metabolism of carbohydrates, the regulation of cellular moisture, and the synthesis of protein amino acids. The improvement of the disease resistance of P. sinensis in China, increased drought tolerance, and changed fruit quality greatly. In the absence of potassium, the color of the peach leaves is light, the leaves are small, and the leaves are crumpling and curling. Sometimes they are rolled into a sickle shape, and the leaf margin is tarry and bitter; the physiological fruit drop rate is high, and the fruit is small in taste. Mild potassium deficiency in the field, no symptoms appear in the early growth stage, and it is easy to show in the later stage of fruit development. (d) Calcium forms the cell wall in the form of calcium pectin, which is necessary for normal cell division and contributes to cell membrane stability. Calcium moves very little in plants. In the absence of calcium, it is first expressed on the roots. The roots are short and dense, the density of hair roots is greater, the root tip is dead, and "root disease" is formed; young leaves at the top of shoots are necrotic from the tip or midrib; It is believed that the later-stage water heart disease is also related to calcium deficiency. (5) Ferro-iron is an essential element for the synthesis and maintenance of chlorophyll. Iron is not easy to move in the peach tree. Iron deficiency begins with the young leaves. The veins remain green and chlorosis between veins. In severe cases, the entire leaves are yellowed until white, with brownish-yellow necrotic spots, and can reach young leaves and tender. Slightly dead. Peach trees are commonly iron-deficient in limestone blocks or severe saline-alkali lands. (6) Boron and boron can promote pollen development, germination, and prolonged growth of pollen tubes, and increase fruit setting rate. Peach is sensitive to boron deficiency. When Peach is deficient in boron, shoot tips and apical growth cones stop growing and browning is dead. During the growth of new shoots, "top wither" occurs, the leaves become thick and brittle, and the fruit surface appears pitted clear spots, and flow plastic, flowers. Anthers are wilting, flowers are poorly fertilized, and fruit setting is low. (7) Zinc peach trees are sensitive to zinc deficiency. In the absence of zinc, the growth of new shoots is blocked, and the leaves are small and brittle. They are clustered together. They are called “lobular leaf disease†(or leaf disease). The flower buds are reduced. The results are few. The fruit is small and the skin is of very poor quality. (8) Manganese manganese has important functions in photosynthesis and participates in the respiratory process. Chinese Peach is sensitive to Mn deficiency. When the Mn deficiency occurs, young leaves and leaves grow to a certain size and show a special chlorosis between lateral veins. Severe deficiency of manganese, necrotic spots between veins. Early leaves, new shoots died, roots undeveloped, fruit color, poor quality, and sometimes split skin. (9) Copper is a component of many important enzymes and plays an important role in photosynthesis. In the absence of copper, the young leaves of the peach tree are narrow and long, and the leaf margins are not even as if they were burned; the new shoots are dead, the leaves are dark, the tip leaves are yellow, the leaves are curled, the edges are broken, and early leaves fall. The growth is weakened, the fruiting is reduced, the quality is poor, and it is sensitive to freezing damage in winter. The physiological effects of the above elements cannot be replaced with each other, but they are also related. Some elements have antagonism, that is, when one element increases, the absorption of another element decreases. Such as nitrogen and potassium, boron, zinc, phosphorus, copper, the increase in nitrogen will inhibit the absorption of these elements of the peach; and if there is antagonism between phosphorus and potassium, magnesium. Therefore, when there is a lack of symptoms on the peach tree, it may not be due to lack of the element, but due to too many additional elements. Sometimes there are several elements that are simultaneously deficient, and peach trees show complex symptoms that are difficult to recognize. Therefore, once there is a deficiency in the tree, it is necessary not only to observe its symptoms, but also to analyze the intrinsic causes of the disease, and sometimes it is necessary to conduct leaf analysis in order to diagnose accurately, so as to take effective and targeted remedial measures. Third, the fertilization period According to the nature of fertilizer and fertilization period, fertilization can be divided into base fertilizer and top dressing. (1) Base fertilizer is the basic fertilizer for supplying nutrients for a long period of the year. Usually based on slow-release organic fertilizers, such as manure, soil manure, green manure, straw, etc., and appropriate addition of superphosphate and nitrogen fertilizer to improve fertilizer efficiency. After applying basal fertilizer, it can increase soil organic matter, improve soil and increase soil fertility. After the fertilizer is gradually decomposed, it can be used for longer-term absorption and utilization of peach trees. The application period of basal fertilizer is good from 9 to 10 months. Since this is the root of the root system at the second peak of growth, the absorption capacity of the root is strong, and the fall fertilizer can have enough time to make the fertilizer mature and can be used by peach trees before they sleep. Autumn basal fertilization will cause part of the root system to cut off, which is equivalent to the pruning of the root system, thus promoting the growth of the root system, increasing the nutrient reserve of the tree body, facilitating the enrichment of flower buds, enhancing the ability to resist overwintering over the winter and the flowering of the following year, Fruit setting also has a good effect, so the autumn basal dressing is better than the fallen leaves and the spring season. (b) Fertilizer is also called supplement fertilizer. That is, on the basis of the Shiji fertilizer, according to the characteristics of the fertilizer needed during the various phenophases of peach trees, the fertilizers will be supplied to meet the needs of fruit setting, new shoot growth and fruit yield and quality improvement in the year, and will lay a foundation for next year's high yield. The time, frequency, type, and amount of fertilization for topdressing should be based on different rootstocks, tree age, reproductive status, cultivation management methods, and environmental conditions, and should generally focus on top dressing in the early growth stage. The saplings and trees with few results can reduce the amount and frequency of topdressing when the basal fertilizer is sufficient. The frequency of top dressing with poor fertilizer and low water retention should be higher. When base fertilizer is used in autumn and the amount of fertilizer is large, the frequency of topdressing can be reduced. Quantity. Fertilization must be timely and can not be applied too late, otherwise it will cause germination to be postponed, physiological fruiting increased; late mature and other adverse effects, should pay attention to this point in production. Combining the several main phenological periods of the Chinese Peach, the characteristics of the fertilization in each period are described as follows: 1. Before and after the germination, the root period of the Chinese Peach Peach begins to be active early in the spring. Therefore, the top dressing before germination should not be later than usual, generally About 1 month before germination should be topdressing. Top dressing is mainly quick-acting nitrogen fertilizer. Properly matching with phosphate fertilizer to supplement the lack of storage nutrients in previous year's tree body promotes neat buds and improves flowering and fruiting ability. 2. Before and after flowering, the germination and flowering process of P. sinensis in China will consume a large amount of storage nutrients. After flowering, it is also a period of rapid growth of young fruit and shoots. At this time, it needs more fertilizer and should be topdressed. The main nitrogen fertilizer is quick-acting, supplemented with boron fertilizer to increase fruit setting rate. During this period, topdressing can be complemented with topdressing before flowering. If the amount of topdressing before flowering is more, no application or less application may be made during this period. 3. The hard nuclear phase is the time when China's Peach has shifted from using storage nutrition to the nutrient made in the current year. Chinese Peach peach has a longer hard core period and requires more nitrogen. At this time, adding nitrogen fertilizer can promote the development of embryos and fruit hypertrophy. Attention should be paid to the ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. Excessive nitrogen may increase the cracking nucleus. 4. Topdressing Topdressing This top dressing is mainly to supplement the nutrient loss caused by the tree and increase the nutrient accumulation of the tree, which is conducive to flower bud differentiation, leaf protection and delayed leaf senescence, and promote root growth. Top dressing should be dominated by nitrogen fertilizer, with phosphorus and potash. Fourth, fertilization methods (a) soil fertilization Fertilization effects and fertilization methods are closely related. Fertilization of soil Fertilizer should be applied as much as possible in the 20-60 cm soil layer where the roots are concentrated in order to absorb the roots and reduce fertilizer loss. Basic basal fertilizers should be applied in soil layers slightly deeper and farther away from the concentrated distribution layer of the root system to induce the extension of the root system to depth and breadth; topdressing, especially quick-acting nitrogen fertilizers, should be applied to soil layers slightly above the concentrated distribution layer of the root system. Inside, it is beneficial to infiltration of fertilizers. The methods commonly used for soil fertigation in production are as follows: 1. Fertilization in the whole garden is suitable for adult peach trees and dense planting Taoyuan, that is, the fertilizer is evenly spread on the ground, and then deep into the soil, the depth is about About 20 centimeters, usually combined with autumn plough or spring plowing. 2. Ring groove fertilization is to excavate an annular groove at the periphery of the canopy. The groove width is 50 to 60 cm and the depth is about 60 cm. After digging the ditch, the fertilizer and soil are mixed and applied uniformly, and the soil is filled. This method is simple, economical with fertilizer, but with a small scope of application, suitable for saplings or digging planted dense planting saplings. 3. Strip fertilization Fertilize at the outer edge of the canopy, or dig 50 to 60 cm wide, 40 to 60 cm deep, and the length is determined by the size of the fertilization ditch. Mix organic manure such as ring fertilizer with the surface layer of mature soil. In the ditch, the heart and soil will be covered in the ditch and in the tree tray. The next year, the fertilization ditch can be changed to the other side, so that it expands year by year until it spreads all over the park. 4. Radial fertilization Fertilization starts from a place about 1 m from the tree trunk, and 3-4 ridges are radially excavated outward from the trunk. The depth of the groove is 20 to 50 cm, and the width is 40 to 60 cm. The length of the ditch exceeds the length of the canopy. Periphery. The ditch is gradually shallower and deeper from the inside to the outside so as to reduce the damage. The position should be changed each year when digging trenches. This method has less roots and more fertilization area, suitable for adult peach orchards in fruiting period. The disadvantage is that it is inconvenient to work in Taoyuan, which is too low, and it is also easy to hurt big roots. 5. Cave storage of fertilizer and water Digging along the outer edge of the tree trunk around the trunk to make it evenly distributed. The number of holes depends on the size of the canopy and the soil conditions. The result is that the trees are usually 4-6, about 30 centimeters in diameter, and 50 centimeters deep. The grass in the caves is about 20 centimeters thick. The length is shorter than the depth of the hole by 3 to 5 cm. When the grass is buried in the hole, the soil is mixed with compound fertilizer and other trace fertilizers in the surrounding soil. After burying, the ground is leveled and a small pit is left at the top of the hole to inject human waste or liquid fertilizer. Inside the hole, cover the mulching film and compact the edges with soil. This method is less suitable for the autumn, less rain, drought and less rain Taoyuan or fertilizer Taoyuan lack of water, this point can be used for a long time, in the peach growth and development of the need for large amounts of fertilizer can be at any time into the fertilizer and water, both labor and water economy High efficiency. The amount of fertilizer should be determined according to the age of the tree, the type of fertilizer, the period of fertilization, and the nature of the soil. While selecting fertilization methods, it is also necessary to determine the location and depth of fertilization according to specific conditions. Fertilization should be applied as close to the root as possible to facilitate root absorption. For young peach orchards, localized fertilization should be adopted because of the small root distribution; during the fruit period, the Taoyuan roots have covered the whole garden. In the case of large amount of fertilizer, the whole garden can be fertilized. If there is little fertilizer or there is an intercropping, local fertilization can be used. Methods. The horizontal roots of peach trees grow more than 1 times more than the canopy, while a large number of roots are concentrated outside the canopy. Therefore, the localized application of fertilizer in adult peach orchard is applied at the outer edge of the crown to induce the outward expansion of the root system. In order to make all parts of the root can get fertilizer, promote the development of the root system, pay attention to change the location of fertilization, and should use different methods of soil fertigation alternately. The depth of fertilization needs to be considered from many aspects, and should be determined according to the distribution depth of a large number of fibrous roots. The vertical distribution of the peach root system is shallow, and the fertilization should be shallow. The phosphorus and potash fertilizers that are difficult to move should be applied deeply; the nitrogen fertilizers that are easy to move should be applied shallowly; the organic fertilizers should be applied deeply; the loams and clays with strong fertility can be applied deeply; The ground should be shallow in the rainy season. (B) In addition to soil fertilization outside the root fertilizer peach, but also a certain amount of fertilizer can be dissolved in water, spray directly on the leaf, can also be used trunk injection method, these fertilization methods known as top dressing. The benefits are rapid fertilizer efficiency and high utilization. The effect of foliar dressing is generally seen in about 10 days after spraying, and the distribution in all types of shoots is even more uniform than that in the roots, which is more favorable for weak branches; Taoyuan and poor soil conditions in Taoyuan and susceptible soils. Fixed elements such as phosphorus, iron, zinc, boron, manganese, etc., the effect of using foliar topdressing method is quick and saves fertilizer; the foliar dressing can be combined with spraying and labor is saved; the inter-planting of peach orchard, when the soil fertilization is inconvenient, the foliar can be carried out top dressing. Although there are many advantages in dressing fertilizers outside roots, they are not used for a long period of time. Generally, they disappear after 20 days. They can only be used as a supplement to soil fertilization. Most of the fertilizers are still supplied through root fertilization. The top-dressing fertilizer should be careful, use the appropriate fertilizer type, concentration and the appropriate time to avoid causing fertilizer damage. When the leaves are wet, the absorption of the sprayed fertilizer is fast. Therefore, the spraying time is best selected on cloudy days or sunny mornings and evenings. Generally before 10 o'clock in the morning and after 4 o'clock in the afternoon, in order to avoid rapid evaporation of high temperatures, the solution quickly concentrated, affecting the spraying effect and causing damage to the leaves. Spraying should be meticulous, thoughtful, both sides of the blade should be even with the liquid, because the back of the leaves absorb faster, do not ignore. V. Fertilization amount The amount of fertilization of Chinese sacred peaches is affected by various factors such as growth results and soil conditions. There are several ways to determine the amount of fertilizer that is suitable for the region: First, investigate. In-depth production practices, extensive investigations of fertilizing amounts of various types of peach orchards, combined analysis of soil and fertility of peach trees, such as tree vigor, yield, quality, etc., were comprehensively analyzed and compared, and the effects of fertilization were summarized to ensure that the tree vigor could be guaranteed. , And can obtain early fruit, high yield, stable and high-quality suitable amount of fertilizer, and then continue to adjust according to the tree reaction in production, making it gradually adapted to local conditions, which is an important way to determine the amount of fertilizer. The second is through the analysis of leaf nutrient elements. Determine the tree's nutritional level as a basis for formulating fertilization. Because the peach leaves are sensitive to the nutrient response, and the sampling is easy, the damage to the logarithm of the collected leaf is also small. The leaf collection analysis is generally performed when the shoots stop growing and the content of nutrients in the leaf changes little. The third is to conduct field fertilization tests based on the above two tasks. The fertilization test is the most scientific method to determine the amount of fertilization, but the fertilization experiment takes a long time, and the fertilization test has obvious regional limitations. Therefore, the fertilization experiment should be carried out in conjunction with specific local conditions to determine the most economical and effective The amount of fertilizer. The theoretical calculation of the amount of fertilizer should consider three factors: (A) The absorption of peach is the amount of nutrients that peaches absorb from the soil. It is generally known from the analysis of the content of each element in each organ. (b) The natural amount of soil supply is known from soil analysis. Generally, nitrogen is 1/3 of the absorption amount of soil supply, and potassium and phosphorus are 1/2 of the absorption amount. (3) The fertilizer utilization rate is the percentage of the peach tree that can actually be absorbed after the fertilizer is removed and the soil is fixed. Fertilizer use efficiency is usually 50% for nitrogen fertilizer, 30% for phosphorus, and 40% for potassium. The relationship between the amount of fertilization and the three factors is as follows: Fertilizer amount = (peach absorption - natural supply) Fertilizer use efficiency However, in fact, peach fertilizer absorption, natural soil supply, and fertilizer utilization are affected by many factors. The influence of factors, therefore, the determination of the amount of fertilizer should be closely combined with nutrition analysis and practice, in a relatively long practice, the scientific value suitable for the local.