Professor Cai Xiujun from the Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine has extensive experience in abdominal surgery, hepatobiliary and pancreatic surgery, minimally invasive surgery, and transplant surgery. His team recently used Arraystar circRNA chips to study androgen in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The effect of receptor (AR) on circRNA expression. It was found that AR can bind to the promoter region of the RNA editing enzyme ADAR1 to up-regulate the transcription of ADAR1 p110, thereby inhibiting the expression of circRNA. At the same time, it was found that patients with high expression of ADAR1 had poor prognosis and positive correlation with AR expression. In addition, circARSP91 is a circRNA regulated by AR-ADAR1 and down-regulated, which can inhibit the growth of HCC tumors in vitro and in vivo. The research results were successfully published in the internationally renowned academic journal Cell Death and Disease (IF: 5.965) in 2017 . (Chip experiments are provided by Kang Cheng Biotech) In order to study the effect of AR on the expression of circRNA in HCC, the authors first detected some circRNAs whose host genes were not regulated by AR by qRT-PCR, and found that RB expression was down-regulated or up-regulated after AR overexpression or knockout. Then the author passes Arraystar  The circ RNA microarray was used to study the expression profile of circRNA in AR-expressing HCC cell line and AR knock-out HCC cell line. The screening showed that there were 331 up-regulated AR after knockout, which was much higher than 177 down-regulated. The difference multiple of the up-regulation is also greater than the difference multiplier of the down-regulation. These results indicate that AR can inhibit the expression of circRNA in HCC. Result display Figure 3, A: circARSP91 is derived from PABC1 exon 9 and is resistant to RnaseR; B: qRTPCR and WB indicate that circARSP91 can be inhibited by AR-ADAR1; C: nude mice tumor formation experiments indicate that circARSP91 can inhibit HCC tumor development; D: AR is a pattern diagram that affects the development of HCC by binding to the promoter region to upregulate ADAR1 expression and inhibit the expression of circRNA. Significance Roughness Measuring Instrument
Roughness meter, also known as surface roughness meter, surface smoothness meter, surface roughness tester, roughness measurement meter, roughness tester, and other names. It has the characteristics of high measurement accuracy, wide measurement range, easy operation, portability, and stable operation. It can be widely used for the detection of various metal and non-metal processing surfaces. This instrument is a pocket instrument that integrates sensors and hosts, with handheld characteristics, making it more suitable for use in production sites. The exterior design is sturdy and durable, with significant resistance to electromagnetic interference, in line with current design trends.
The application fields of roughness meters include: Roughness Measuring Instrument,Surface Roughness Tester,Roughness Tester,Mitutoyo Roughness Tester Zhejiang dexun instrument technology co., ltd , https://www.dexunmeasuring.com
Research Background
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a heterogeneous malignancy caused by complex genetic and epigenetic changes and is the second leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. HCC is characterized by significant gender differences, but its mechanism is not yet clear. The role of androgen receptor (AR) in gender differences in the development and progression of HCC has been reported in the literature. In addition, circular RNA (circRNA) is a new class of non-coding RNA molecules that exert biological functions and influence the development of diseases such as cancer through various mechanisms. The adenosine deaminase ADAR1 acting on RNA can promote the development of HCC by interrupting RNA editing. It is also reported that ADAR1 is a key regulator of circRNA formation. However, the potential functions and molecular mechanisms of circRNAs regulated by RNA editing enzymes in HCC are still poorly understood.
The purpose of this study was to investigate the inhibition of circRNA expression by RNA editing enzyme ADAR1 in HCC by circRNA microarray, thereby affecting HCC, and experimentally studying the mechanism of this regulation through a series of functional mechanisms.
Research ideas
Next, the authors found through qRT-PCR and WB experiments that AR can up-regulate the expression of RNA editing enzyme ADAR1 p110 mRNA and protein, and ADAR1 knockdown can restore the expression of arRNA inhibited by AR. Subsequently, by analyzing the data in the TCGA database and WB and immunohistochemical analysis, it was found that ADAR1 was up-regulated in HCC and positively correlated with AR. In addition, qRT-PCR revealed that CRC expression was down-regulated in HCC patients. These results indicate that AR can inhibit the expression of circRNA in HCC by up-regulating ADAR1 p110. At the same time, KM curve analysis showed that high expression of ADAR1 predicted poor prognosis and was more likely to relapse and progress. Next, the authors confirmed that AR can bind to the ADAR1 p110 promoter region and activate its transcription by biosignal analysis, ChIP and luciferase reporter experiments.
Finally, the authors verified that the expression of AR was more than 5-fold and the five circRNAs from the same gene PABPC1 were verified. It was found that circARSP91 derived from exon 9 was resistant to RNase R digestion, and subsequent studies found that AR inhibited by ADAR. Its expression. Colony formation experiments, MTT and nude mice tumor formation experiments showed that circARSP91 can inhibit tumor growth.
Technical route  Â
  Â
Â
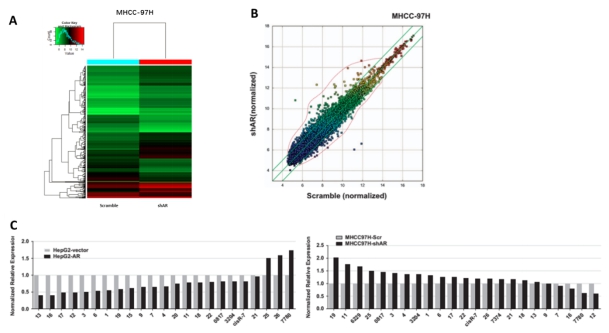
Figure 1. A: cluster map of Arraystar circRNA chip screening; B: scatter plot of Arraystar circRNA chip screening; C: qRT-PCR showed that AR inhibits the expression of circRNAs. 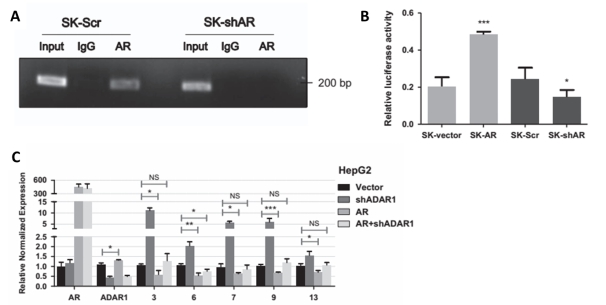 Â
Â
Figure 2, A: ChIP indicates that AR can bind to the ADAR1 promoter region; B: luciferase assay indicates that AR can promote high expression of ADAR1 in HCC; C:qRTPCR indicates that ADAR1 knockdown can restore AR-inhibited circRNA expression. 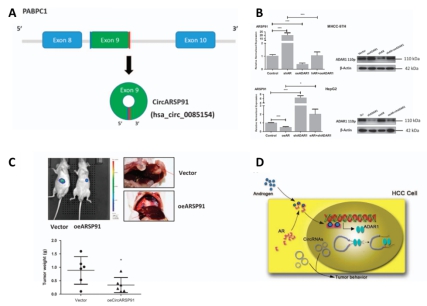 Â
Â
The results of this study indicate a novel feature of CRC expression pattern in HCC, that is, AR can up-regulate the expression of ADAR1 p110 by binding to the promoter region of ADAR1, thereby inhibiting the expression of circRNA and affecting the development of HCC. This pattern of expression of circRNA helps to explain the apparent gender differences in HCC from a new perspective. At the same time, we have discovered a new circular RNA circARSP91, which can effectively inhibit the formation of HCC tumors in vitro and in vivo, and help to better understand the role of circRNA in the development and progression of HCC, which is also the search for HCC through circRNA. The new treatment laid the foundation.
Original source
Circular RNA expression is suppressed by androgen receptor (AR)-regulated adenosine deaminase, acts on RNA (ADAR1) in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death and Disease. 2017. 
1. Mechanical processing and manufacturing industry, mainly metal processing and manufacturing. Roughness meters were originally developed to detect the surface roughness of machined parts. Especially, stylus type roughness measuring instruments are more suitable for detecting hard metal surfaces. For example, the automotive parts processing and manufacturing industry, the mechanical parts processing and manufacturing industry, and so on. As long as these processing and manufacturing industries involve the surface quality of workpieces, the detection application of roughness meters is essential.
2. In the non-metallic processing and manufacturing industry, with the progress and development of technology, more and more new materials are applied to processing processes, such as ceramics, plastics, polyethylene, etc. Some bearings are now made of special ceramic materials, and pump valves are made of polyethylene materials. These materials have a hard texture, and some applications can replace metal materials to make workpieces. During production and processing, their surface roughness also needs to be tested.
3. With the continuous strengthening and improvement of the technology and functions of roughness meters, as well as their in-depth promotion and application, more and more industries have been found to require roughness detection. In addition to mechanical processing and manufacturing, roughness evaluation is also required in the production and processing of power, communication, electronics, such as couplings on switches, integrated circuit semiconductors, and even stationery, tableware, and other products used in people's daily lives The surface roughness of human teeth needs to be tested.