Establishment of a mouse model of asthma sensitization and isolation of spleen CD4+ T cells Establishment of sensitized asthma model in mice and CD4+T lymphocyte isolation  From spleens Cheng Xiaoming , Wang Changzheng , Li Shuping , Qian Guisheng ( Institute of Respiratory Medicine, Xinqiao Hospital, Third Military Medical University , Chongqing 400037 , China) Abstract : Objective To establish a reliable mouse model of asthma sensitization and isolate spleen CD4+ T cells. Methods ovalbuminsensitized process model, isolated CD4 + T cells using panning method. Results The lung tissue of this model showed typical pathological changes of asthma . The percentage of eosinophils (EOS%) in peripheral blood and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF ) was significantly higher than that in the normal control group (P < 0.01) . CD4 + T cell purity by flow cytometry (FCM) in a purity of 97.3%. Conclusion The model established by this method and the isolated CD4+ T cells can be used for experimental studies of asthma. Establishing an animal model of asthma and isolating high-purity CD4+ T cells is an important prerequisite for experimental study of the pathogenesis of asthma. This experiment introduces the establishment of a mouse sensitization model and the isolation of spleen CD4+ T cells. 1 Materials and methods 1.1 main reagents and materials 1.1.1 lymphocyte separation medium will be 9% ficoll 400 solution (Sigma) and 33.9% diatrizoate was mixed solution, to adjust the specific gravity 1.090. 1.1.2 Preparation of nylon hair column Weigh 80mg nylon wool , carefully peel it into a 2 ml disposable syringe , the column height is about 4 cm . Hanks' solution sufficiently wetted with nylon wool column, without leaving air bubbles inside it, sterilized by autoclaving. The column was washed with RPMI 1640 ( containing 10% fetal bovine serum , Fetal calf serum, FCS) pre-warmed to 37 °C before use and the lower end outlet was closed. 1.1.3   CD8 + monoclonal antibody (Monoclonal antibody, mAb) preparing several coated plates taken polystyrene plates, the CD8 + mAbs solution (Beijing bonding Company) 100 μ l added to dish, and adding 0. 05 mol / L of carbon 3 ml of acid salt buffer (pH 9.5), mix well , stand aseptically for 40 min at room temperature, rinse with phosphate buffer (PBS, pH 7.2) , add PBS containing 1% FCS , and incubate at room temperature for 15 Min, rinse with PBS , and store at 4 °C for later use. 1.2 Experimental animals and grouping 4-6 periodontal health of BALB / c mice 40, male or female, weighing 16 ~ 20 g, supplied by Experimental Animal Center, Third Military Medical University. The mice were randomly divided into two groups, A is a group of normal control group with saline instead of chicken egg albumin (Ovalbumin, OVA, Grade Ⅱ, Sigma Co.) sensitized and challenged mice; Group B was sensitized model group, to give OVA is sensitized and stimulated. 1.3 Establishment of a sensitized mouse model Respectively, on day 1, day 13 the mice were injected intraperitoneally 10 μ g OVA and aluminum hydroxide gel (Al (OH) 3) 20 mg mixture; day 25, each mouse was placed individually 5 L closed container to be 1% OVA inhalation excitation, the mice were exposed to aerosolized OVA in 20 ~ 30 min until the onset of asthma-like far for 6 d. The atomization power is provided by the 402 type ultrasonic atomizer ( Shanghai Heli Medical Instrument Factory ) . 1.4 peripheral blood, bronchoalveolar lavage ( Bronchoalveolar lavage Fluid, BALF) percentage of eosinophils (percentages Of eosinophils, EOS %) count and lung tissue specimens 1.4.1 EOS% in peripheral blood and BALF Groups of mice each count most 14 After excitation time 24 h, intraperitoneal anesthesia, tracheotomy was collected BALF 5ml, 5 至 0. 8 ml 。 Acupuncture the heart to take blood from about 0. 5 ~ 0. 8 ml . Centrifuge all the liquid and collect the fine precipitate Cells , add red blood cell lysate to remove red blood cells. With a solution of EOS EOS line count number. 1.4.2 lung tissue samples without opening the bronchial specimens in each group of 6 mice each pleural lavage, lungs were observed substantially changed, the clipping part of the lung tissue, the sections were fixed in 10% formalin, stained with HE. 1.5   Isolation and identification of CD4+ T cells 1.5.1   Isolation of CD4+ T cells The mouse peritoneal cavity was opened , the spleen was aseptically removed and placed in cold Hanks solution , which was mashed and filtered through a 100 mesh sterile steel mesh , and the spleen cell suspension was collected and added to the lymphocyte separation solution , 2 000 g was centrifuged 30 min, gently aspirate the intermediate wall along the gray cell layer 1640 was resuspended in RPMI containing 10% FCS; and 1 × 108 cells per added nylon wool column, 37 ℃, 5% CO2 incubator Incubate for 1 h in the chamber ; open the lower end outlet , let the T cell suspension flow out at 40 to 60 drops (Drop, d) / min , wash the column repeatedly with RPMI 1640 solution to the eluate up to 6 ~ 8 ml, and then suspend the cell suspension. every 1 × 107 to join the CD8 + mAb-coated polystyrene dishes, and RPMI 1640 solution was added 2 ml, mixing, effect. 4 deg.] C 70 min, shaking every 20 minutes once a gently rotating, draws along the wall plate cell suspension and washed twice with a solution of 1640 light RPMI, 2 000 g was centrifuged 10 min, i.e., the cell suspension collected CD4 + T cells. After trypan blue count , cell viability was > 89% . 1.5.2   Purity Identification of CD4 + T cells by flow cytometry (Flow cytom2etry, FCM) Identification of CD4 + T cells Purity [1]. 1.6 statistical analysis         The results of each group were expressed as ?x ± s , and the unpaired t test was used for comparison between groups . 2 results 2.1 Pathological changes of lung tissue in mouse sensitization model       The lungs of the sensitized mice showed a significant increase in volume compared with the lungs of the normal control mice , and the surface was swollen with a number of irregularly dark red blood-filled areas. White foam section exudate, and blood vessel cross-section can be seen clearly. HE staining of lung and bronchial seen a large number of perivascular inflammatory cell infiltration, mainly in EOS, pulmonary interstitial and alveolar infiltrates EOS can also be seen. Mucus plugs are visible in the tiny bronchi. The airway epithelium is broken at many places , and the basement membrane is obviously thickened and irregular in shape. Hypertrophic hyperplasia occurs in the bronchial smooth muscle. 2.2 peripheral blood and BALF EOS% 2.2.1 Peripheral blood EOS% sensitized mice had a significant increase in peripheral blood EOS% (11.0 ± 2.7) compared with the normal control group (0.7 ± 0.5) (P < 0.01) . 2.2.2   BALF EOS% in BALF of mice in the control group almost no EOS (0.0 ± 0.01), in BALF of sensitized mice EOS% (21. 9 ± 4. 4) and the normal control group was significantly higher (P <0.01 ) . 2.3   CD4+ T cell purity identification results Detected by FCM, CD4 + T cell purity was 97.3%, see figure 1. 3 discussion The established BALB / c mouse model of pathological sensitization is: lung edema, small, small bronchi how the amount of the mucus plug, airway epithelial broken off, thickening of basement membrane, blood vessels in lung peribronchial EOS based inflammatory cell infiltration, similar to the pathological features of asthma; the same time, this model mice peripheral blood and BALF increased significantly EOS%, consistent with asthma and peripheral blood in BALF EOS% change, indicating that this The model can be used for experimental studies of asthma. The Panning method is also known as the washing method. It is a method for cell separation using the principle of combining antigen and antibody . It has the characteristics of simplicity , economy and good cell integrity. Foreign early 1990s, this method is widely used in the upcoming mid-term experiments. With the continuous advancement of science and technology , the methods used to separate cells abroad are mainly magnetic bead separation [2] and flow cytometry [3], but their cost is expensive , and it cannot be used in China. It is generally carried out , so using Panning to separate cells is still an efficient and economical method. In this experiment , CD4+ T cells isolated by Panning method were detected by FCM and have high purity , which can be used for further experimental research. Keywords : asthma ; model ; mouse ; CD4+ T cells Chinese Library Classification : R - 332; R562.25 Document ID : B References : [1] Shen Guan , Zhou Qilin . Experimental techniques of modern immunology [M]. Wuhan : Hubei Science and Technology Press , 1998.180 - 183. [2] Holmes B J , MacAry P A , Noble A , et al. Antigen 2 specific CD8 + T cellsinhibit IgE responses and interleukin24 production by CD4 + Tcells [J ]. EurJ Immunol , 1997 , 27(10) : 2 657 - 2 665. [3] Denkers E Y, Scharton 2Kersten T, Barbieri S, et al. A role for CD4+NK1.1 + T lymphocytes as major histocompatibility complex class II inde2pendent helper cells in the generation of CD8+effectorsfunction against in2tercellular infection[J]. J Exp Med, 1996, 184(1): 131 - 139. ( Editor Chen Conglian ) Starch Empty Capsule,Starch Empty Capsule Shell,Starch Clear Pill Capsules Empty,Starch Hard Empty Capsule Ningbo Jiangnan Capsule Co., Ltd. , https://www.jncapsule.com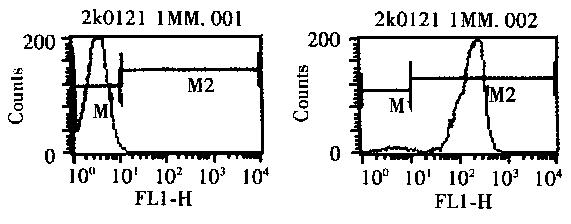 Figure 1   FCM detects the purity of CD4+ T cells
Figure 1   FCM detects the purity of CD4+ T cells