Conventional Photoelectric Smoke Detector Conventional Photoelectric Smoke Detector,Carbon Dioxide Detector,Fire Detector,Smart Smoke Detector NINGBO TOMAN IMP. & EXP. CO., LTD , https://www.tdotmfiresolution.com
Hepatocellular carcinoma HCC is one of the common malignant tumors in humans, ranking fifth in the incidence of malignant tumors. The 5-year mortality rate of hepatocellular carcinoma is still high due to difficulties in early diagnosis and poor response to various treatments. Although recent studies on early diagnosis of liver cancer and treatment of liver cancer have made great progress, the treatment of liver cancer is still limited. Non-coding RNA plays an important role in cancer biology, providing potential therapeutic targets for liver cancer. Some endogenous non-coding RNAs, such as circRNA, play an important role in development, cellular function, and specific pathological responses. In particular, circRNA can act as a microRNA sponge to regulate gene expression. The study of dysregulated circRNAs and their function in cancer has attracted increasing attention.
To study the expression and function of circRNA in hepatocellular carcinoma. The researchers used Arraystar Human circRNA microarray to study the differential expression of circRNA in 7 cases of hepatocarcinoma and 7 cases of normal liver tissue, and screened 20 differentially significant CircRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma for cluster analysis (10 of which were up-regulated by circRNA, 10 CircRNA down-regulation), qPCR verified that these 20 circRNAs were consistent with the chip results. circMTO1 (has_circRNA_0007874/has_circRNA_104135) was significantly downregulated in HCC tissues. Compared with normal liver tissue, circMTO1 expression was significantly decreased in 87.4% (228/261) of liver cancer tissues and correlated with the degree of malignancy in HCC patients. It was predicted by Miranda that circMTO1 binds to 99 microRNAs; FISH and RIP validate bioinformatics predictions that circRNA can bind to miR-9. Overexpression or knockout experiments indicate that circMTO1 affects the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma, and in vivo experiments have confirmed this result. LOF/GOF circMTO1 found that circMTO1 can act as an adsorption sponge for microRNA binding to the oncogene miR-9 to up-regulate the expression of p21 and inhibit the growth of HCC. Therefore, low expression of circMTO1 can be used as a prognostic target for the treatment of biomarkers and potential HCC patients. 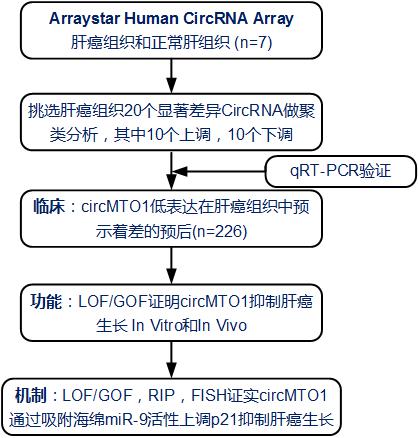
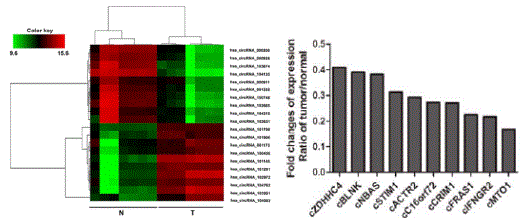
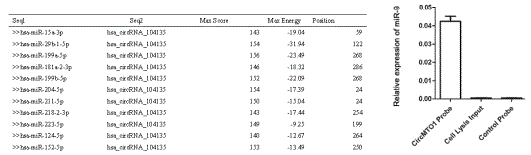
Figure 2: Prediction of circRNA binding to 99 microRNAs by Miranda; FISH validation of bioinformatics predictions 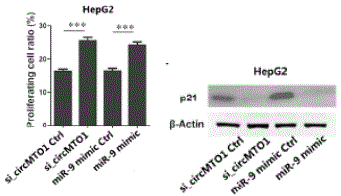
This study used the Arraystar CircRNA chip to study the expression and function of liver cancer tissues. The expression of circMTO1 was found to be significantly reduced in the HCC group and was associated with poor prognosis in HCC patients. Functional and mechanistic studies found that circMTO1 adsorbs miR-9 through sponge and up-regulates the expression of p21 to inhibit the growth of HCC, which means that circMTO1 plays a role as a tumor suppressor gene during the development of HCC. Further, in vivo intervention in the circMTO1 experiment indicated that circMTO1 has the potential for HCC targeted therapy. The results indicate that circMTO1 may serve as a diagnostic marker for prognosis and a target for HCC therapy.
Cao Xuetao, male, academician of Chinese Academy of Engineering, professor, doctoral tutor. Dean of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, President of Peking Union Medical College, Director of the Institute of Immunization of the Second Military Medical University, Director of the Institute of Immunization of Zhejiang University. The head of the National 973 Immunology Project and the National Natural Science Foundation of China. In 2005, he was elected as an academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering. In 2013, he was elected as a foreign academician of the German Academy of Sciences. The main research direction is the basic immunology and the discovery of new genes and the research of immune new molecular functions, the basic and clinical research of tumor immunotherapy and gene therapy with emphasis on dendritic cells. The author of the communication published more than 230 SCI papers in Cell, Nature, Science, Nature Immunology, Cancer Cell, etc. SCI cited more than 6,000 times.
Han D, Li J, Wang H, et al. Circular RNA MTO1 acts as the sponge of miRâ€9 to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma progression[J]. Hepatology, 2017.
Http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/hep.29270/full
Academician Cao Xuetao, director of the Institute of Immunization of the Second Military Medical University and dean of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, is mainly engaged in the basic research of natural immunity and immune regulation and the application research of immunotherapy. Recently, its laboratory using Arraystar CircRNA chip found that circMTO1 can act as a microRNA adsorption sponge combined with oncogene miR-9 to up-regulate the expression of p21 and inhibit the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The research results were published in the international top journal Hepatology ( impact factor 11.71 ). ( Chip experiments are provided by Kang Cheng Biotech )
Research Background:
Research ideas:
Technical route
Result display
Figure 1: Choosing 20 differentially significant CircRNAs in liver cancer for cluster analysis; qPCR verified that the results of circMTO1 chip were consistent with qPCR results.
Figure 3: CircRNA inhibits the activity of p21 by up-regulating miR-9 by microRNA sponge to inhibit liver cancer
Significance
Corresponding author profile
Original link