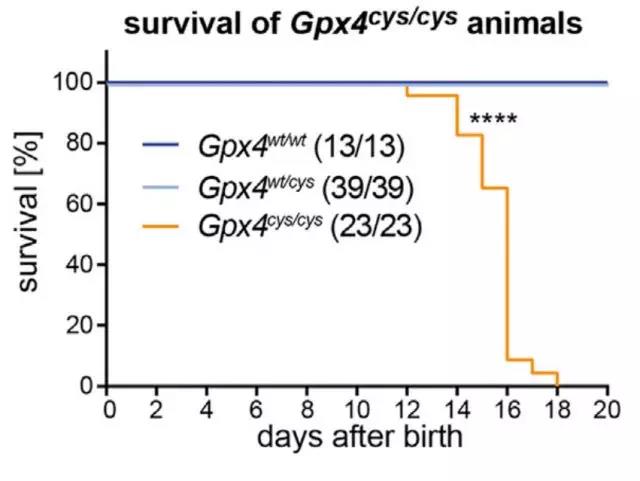
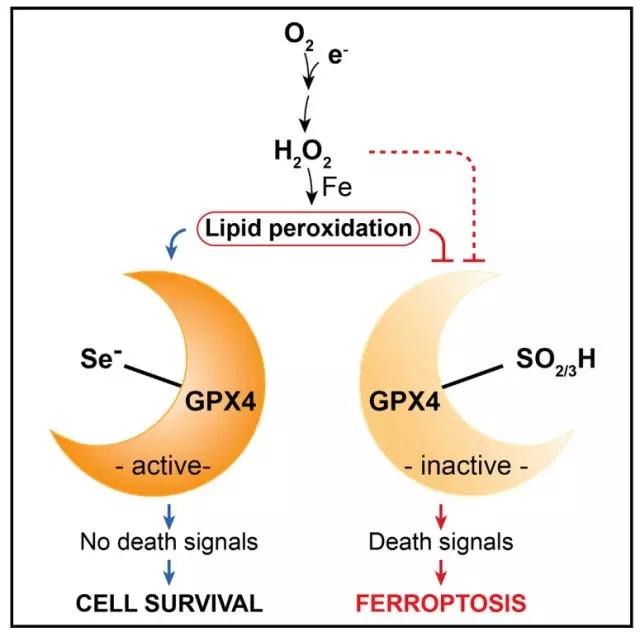
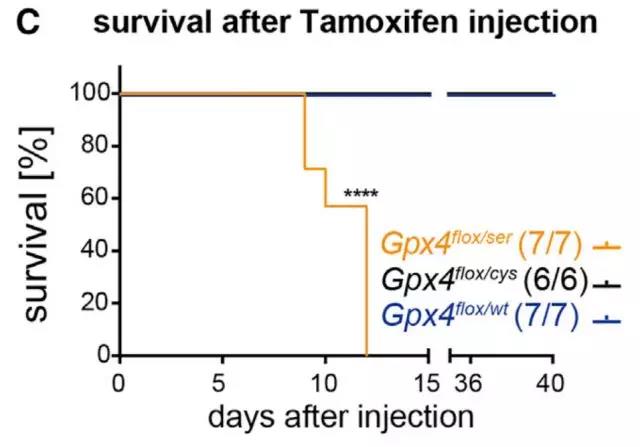
Release date: 2018-01-23 Selenium is one of the eight trace elements necessary for the human body currently identified. Asking about the mother, we will find that the trace element selenium has been given the "king of anti-cancer" "bright messenger" "the patron saint of the heart" "natural enemies of liver disease" "gold in the body of men" "trace elements A series of titles such as insulin. Obviously, the influence of selenium in the health care field has far exceeded our imagination. But is selenium really worthy of so many titles? Recently, the team of Dr. Marcus Conrad from the Institute of Developmental Genetics at the Helmholtz Center in Munich, for the first time in Cell magazine, clarified the real reason why trace element selenium is indispensable for mammals. They found that during the development of mice, the development of an important interneuron in the brain is highly dependent on the presence of selenium. In the absence of selenium, the content of such neurons is greatly reduced, causing fatal epilepsy, resulting in the death of all mice in the experimental group. In addition, in other periods of mouse growth and development, the lack of selenium does not affect the life, survival and reproduction of mice. Dr. Conrad 200 years ago, Swedish scientist Jons Jacob Berzelius first discovered the presence of selenium and named it the moon goddess Selene. Obviously, the future performance of selenium is worthy of the title of the moon goddess, because it does bring people unlimited beauty. Although selenium was discovered at the beginning, it has been treated as a poison. At that time, it was found that horses were exposed to selenium-enriched soil and there was a phenomenon of horseshoe necrosis and hair loss. But by 1957, scientists have shown that low doses of selenium can also prevent liver necrosis in mice. Since then, it has been known that high doses of selenium are toxic, but low levels of selenium may be beneficial to mammals. Subsequently, a series of fantastic health functions of selenium were dug up in animal experiments, including various anti-cancers mentioned above, improving immunity, improving fertility, protecting the heart, liver and so on. Some scholars have found that selenium is indispensable for the normal development of embryos. Selene statue But the good reverie is finally surviving the cruelty of reality. Not to mention the specific mechanism by which selenium plays the above functions, subsequent studies have shown that the function of selenium may be exaggerated. First of all, take the most attention-anti-cancer function of all the functions of selenium. Previous studies have shown that selenium can reduce the risk of prostate cancer. However, the largest clinical trial to date (including 35,533 men over the age of 50) showed that supplementation of 200 micrograms of selenium per day did not reduce the incidence of prostate cancer during the 5-year follow-up period. In this trial, Dr. Conrad's research not only reveals that the only indispensable function of selenium in mammals is to maintain the normal development of a group of important interneurons; at the same time, combined with previous research, this The discovery also means that a large amount of selenium supplement may actually promote the development of cancer. Blocky selenium Selenium plays a role in the synthesis of selenocysteine ​​in mammals mainly by substituting sulfur on cysteine. In mammals, more than 20 proteins contain selenocysteine, which is also known as selenoprotein. Among all selenoproteins, the most widely studied and most important one is glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4). Previous studies have shown that either the inhibition of selenocysteine ​​transport RNA or the direct knockout of the mouse GPX4 gene directly causes mouse embryos to die until a specific period of time. Similarly, tissue damage caused by knocking out selenocysteine ​​transport RNA or GPX4 in a tissue is very similar. Therefore, it is speculated that selenoprotein GPX4 is the most important carrier for selenium to function in mammals. Dr. Conrad has long been committed to the study of selenoproteins, but in Dr. Conrad's view, since the above experiments were all done by knocking out the GPX4 gene, this does not prove that selenium is indispensable for mammals because the selenium atoms in GPX4 can Replaced by sulfur. Therefore, in this experiment, Dr. Conrad established a special mutant mouse model in which the selenium atoms in the GPX4 protein were all turned into sulfur to explore the true role of selenium. By experimenting with these mice, Dr. Conrad found that, unlike previous studies, the embryos of these mice did not die immediately after the lack of selenium, but normal development, and also produced normal offspring. However, about 14 days after birth, these mouse offspring began to develop abnormalities. It is shown that the weight of the offspring of these mice began to decrease compared to the wild mouse offspring; at 18 days, the offspring of the mice lacking selenium all died of fatal epilepsy. At 18 days, all sulfur-substituted GPX4 mice died (yellow) Since the excitability of the central nervous system of the brain is regulated by important interneurons, small albumin-positive neurons, and mouse small albumin-positive neurons develop mainly at 8-16 days after birth. Therefore, Dr. Conrad suspects that fatal epilepsy in mice may be associated with such neuronal developmental abnormalities. Subsequent further studies found that GPX4 is critical for the developmental maturation of small albumin-positive neurons in mice after birth. Because such interneurons are abnormally sensitive to oxidative stress during development, iron death is easily affected by oxidative stress (a newly discovered pattern of cell death is associated with iron ions). When the selenium atom in GPX4 is replaced by sulfur, the activity of GPX4 is significantly reduced, and the peroxide accumulated in the cells of the small albumin-positive neurons cannot be effectively removed, which induces the death of a large number of neurons, eventually leading to severe epilepsy, resulting in small The mouse died. Selenium atoms are indispensable for GPX4 to prevent oxidative stress-induced iron death Finally, Dr. Conrad also confirmed in adult mice that adult mice do not die after replacing the selenium atoms in all GPX4 in the body with sulphur, and can survive as wild mice. At the same time, cell experiments have also shown that replacing the selenium atom in GPX4 with sulfur does not affect the normal proliferation and differentiation of cells. This means that selenium in GPX4 is only important for mammals during a particular developmental period. Adult mice (black) that replace GPX4 with a sulfur atom can survive as wild mice (blue) All in all, this study demonstrates for the first time the real reason why trace element selenium is indispensable for mammals. In particular, since this paper demonstrates that selenium is critical for the activity of GPX4, previous studies have shown that for leukemia and kidney cancer, the survival of cancer cells is highly dependent on the activity of GPX4. In this way, a large amount of selenium supplement may also promote the progress of cancer by enhancing the activity of GPX4. Reference materials: 1.Ingold I, Berndt C, Schmitt S, et al. Selenium Utilization by GPX4 Is Required to Prevent Hydroperoxide-Induced Ferroptosis [J]. Cell, 2017. 2.Berzelius J J. Unders? Kning af en ny Mineral-kropp, funnen i de orenare sorterna af det i Falun tillverkade svaflet [J]. Afhandlingar i fysik, kemi och mineralogi, 1818, 6: 42-144. 3. Franke K W. A new toxicant occurring naturally in certain samples of plant foodstuffs. 1. Results obtained in preliminary feeding trials [J]. Journal of Nutrition, 1934, 8: 597-608. 4. SOHWARZ K, Foltz C M. Factor 3 activity of selenium compounds [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1958, 233: 245-251. 5. Hatfield DL, Tsuji PA, Carlson BA, et al. Selenium and selenocysteine: roles in cancer, health, and development [J]. Trends in biochemical sciences, 2014, 39(3): 112-120. 6.Matsui M, Oshima M, Oshima H, et al. Early embryonic lethality caused by targeted disruption of the mouse thioredoxin gene[J]. Developmental biology, 1996, 178(1): 179-185. 7. Lippman SM, Klein EA, Goodman PJ, et al. Effect of selenium and vitamin E on risk of prostate cancer and other cancers: the Selenium and Vitamin E Cancer Prevention Trial (SELECT) [J]. Jama, 2009, 301 ( 1): 39-51. 8. Wirth EK, Bharathi BS, Hatfield D, et al. Cerebellar hypoplasia in mice lacking selenoprotein biosynthesis in neurons [J]. Biological trace element research, 2014, 158(2): 203-210. 9. Schwaller B, Tetko IV, Tandon P, et al. Parvalbumin deficiency affects network properties resulting in increased susceptibility to epileptic seizures [J]. Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience, 2004, 25(4): 650-663. 10.Yang WS, SriRamaratnam R, Welsch ME, et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4[J]. Cell, 2014, 156(1): 317-331. Source: Singularity Network Eas anti-theft antenna is mainly suitable for large supermarkets, shopping malls, bookstores, audio stores with Security hard tags, rf soft label, AM lable,Pin and Lanyard, eas detacher, Hook Lock,EAS Self Alarm Tag, EAS Safer Box,etc. Rf Label ,Eas Rf Label,Rf Soft Tag,Rf Security Labels ZHEJIANG BOSHINE ELECTRONIC SECURITY CO.,LTD , https://www.boshine.com