Li Chunli Peng Xing Thermo Fisher Scientific (China) Co., Ltd. Foreword <br> Vegetables are essential foods in people's daily lives, and their daily consumption and market demand are huge. In the process of vegetable planting, in order to improve the yield of vegetables and improve their quality, the application of pesticides is inevitable. Due to the lack of common sense and regulatory measures, there are irregularities in the use of pesticides, such as abuse and misuse, and the choice of growers in pesticides. It tends to be cheap and efficient pesticides, while ignoring the toxicity and high residue of pesticides. In addition, in order to increase the yield and quality of fruits and vegetables, and reduce losses during planting, picking, transportation and storage, growers often A variety of highly toxic pesticides are used in combination, and the amount and frequency of application are increased. This not only causes pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables to exceed the standard, but also aggravates the residues of pesticides in the surrounding environment of the production area, forming a vicious cycle that is difficult to reverse. Many countries and international organizations (CAC, EU, USA, Japan, and China) have strict regulations on the maximum residue limits (MRLs) of pesticides [1]. The problem of pesticide residues in vegetables has not only become a serious challenge in the field of food safety, but also restricts the import and export trade of vegetable products in China [2][3]. Therefore, pesticide multi-residue detection methods have become the focus of research at home and abroad, and many detection techniques have emerged. Experimental part Instrument method Sample preparation method Experimental results and analysis references Interventional Accessories,Introducer Sheath,Introducer Sheath Kit,arterial sheath introducer Anesthesia Medical Co., Ltd. , https://www.jssinoanesthesia.com
Organophosphorus, organochlorine and pyrethroid pesticides are commonly used pesticides, including a variety of highly toxic, highly toxic pesticides and banned pesticides in China. China has promulgated GBNY/T 761-2008 “Determination of organophosphorus, organochlorine, pyrethroid and carbamate pesticide residues in vegetables and fruits†[4]. This experiment was carried out according to this standard, using Thermo Fisher Scientific's new generation triple quadrupole gas chromatography mass spectrometer (TSQ 8000Evo) combined with the corresponding pesticide residue screening method package (670 compounds mass spectrometry information) in the sample The organophosphorus, organochlorine, and pyrethroid pesticide residues are screened, and the corresponding pesticides contained therein are confirmed and quantified.
Instruments and Reagents Mass Spectrometer: TSQ8000Evo Mass Spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA);
Gas Chromatograph: Trace 1310 Gas Chromatograph with AI 1310 Autosampler (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA);
Column: TG-5SILMS 30 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 μm capillary column;
Reagents: n-hexane, acetone;
Chromatographic method programmed temperature gradient: 40 ° C (maintained for 1.5 min), 25 ° C / min to 90 ° C (maintained for 1.5 min), 25 ° C / min to 180 ° C (maintained for 0 min), 5 ° C / min to 280 ° C (maintained 0 Min), 10 ° C / min to 300 ° C (maintained for 5 min)
Inlet temperature: SSL (270°C) Splitless
Carrier gas flow rate: 1.2 mL/min (constant current)
Transmission line temperature: 280 °C
Injection volume: 1.0 μL
Mass spectrometry
Ion source temperature: 300 °C.
Timing scan-SRM mode (Timed -SRM) combined with RT-Alignment function.
Qualitative screening and quantitative detection of pesticide residues were carried out using the Thermo Fisher Pesticide Residues Package (containing 670 pesticide compounds for mass spectrometry).
Pre-experimental treatment methods refer to NY/T 761-2008 “Determination of organophosphorus, organochlorine, pyrethroid and carbamate pesticide residues in vegetables and fruitsâ€.
The specific pre-processing methods are as follows:
Take the edible part, after being shrunk, chop it, mix it thoroughly and put it into the food processor to pulverize it to make the sample to be tested; accurately weigh 25.0 g, add 50.0 mL of acetonitrile, homogenize for 2 min at high speed, and filter. Add 5-7g of sodium chloride to the filtrate, shake and let stand; take 10 mL of the supernatant, heat in a water bath at 80 °C, concentrate to dryness with nitrogen or air; add 2.0 mL of acetone, transfer to 15 mL, wash with 3.0 mL of acetone three times. Make up to 5.0 mL and pass the 0.2 μm filter for testing.
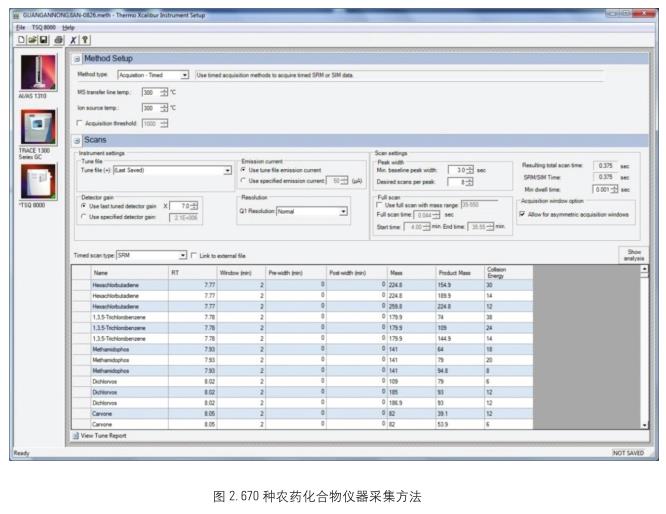
Rapid screening method established The <br>Pesticide Residues package contains information on the optimization of 670 pesticide compounds, including ion pairs (parent and daughter ions), collision energy, scan time, residence time, and number of monitored reactive ions. A series of mass spectrometry parameters. Using the high-speed scanning of the TSQ8000Evo GC/MS, the unique Timed-SRM mode is used to quickly establish the instrument acquisition method, as shown in Figure 1, Figure 2. 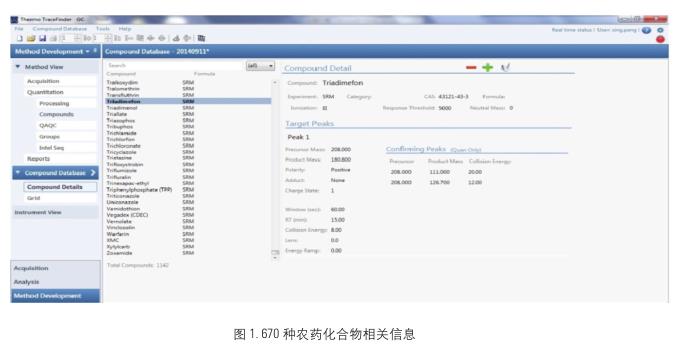
Pesticide identification method
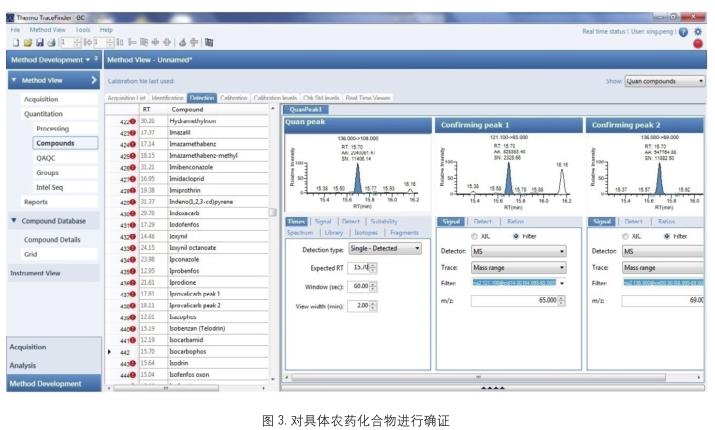
Trace Finder software combined with the Pesticide Residues package provides direct and fast data processing methods. The data collected from the samples are processed quickly to determine the specific species of pesticides and the corresponding retention times. As shown in Figure 3.
Screening method verification <br>Firstly, the above established rapid screening method was applied, and the standard organic phosphorus (concentration 8 μg/kg), organochlorine and pyrethroids (concentration 10 μg/kg) were added to the substrate for data collection. Using Trace Finder for data processing, 18 organophosphorus pesticides and 17 organochlorine and pyrethroid pesticide ion pairs were identified, as shown in Table 1. According to the confirmed pesticide information optimization instrument acquisition method, the actual sample is quantitatively analyzed and analyzed, the standard curve is established by the matrix standard sample, and other samples are quantified. A total of 12 actual samples were tested (according to the standard, organophosphorus, organochlorine and pyrethroid pesticides were sampled separately. There were 2 concentrations per sample, 3 parallel samples per concentration).
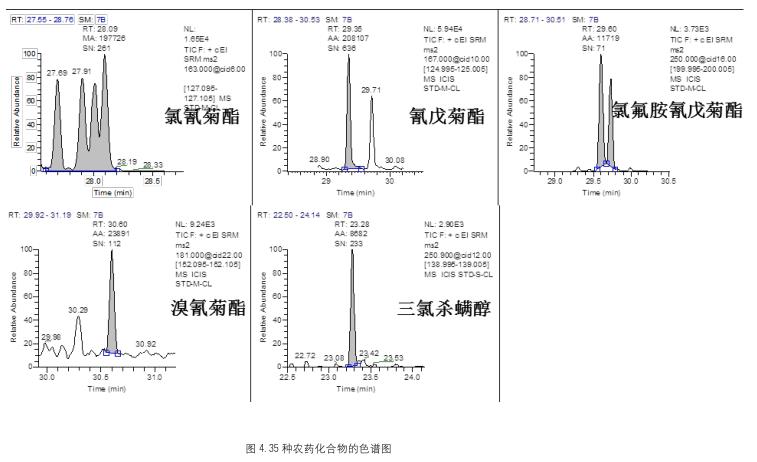
Chromatographic Separation Results <br>The TG-5SILMS column used in the experiment has a good separation effect on pesticide compounds. 35 kinds of pesticides substrate 2 standard (concentrations ≤ 10 μg / kg) in both samples a good chromatogram obtained, as shown in FIG. This experiment ensures the separation of pesticide compounds, avoids the influence of interfering substances in the matrix, and makes the qualitative results meet the method requirements, which is real and reliable. 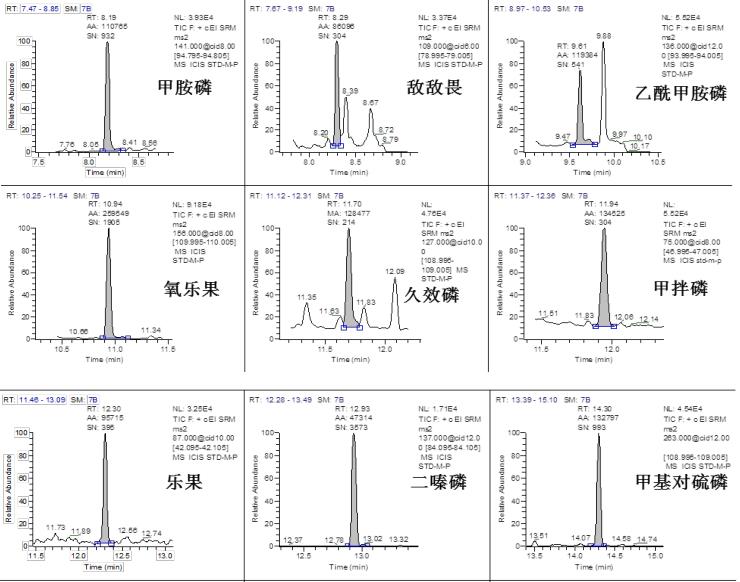
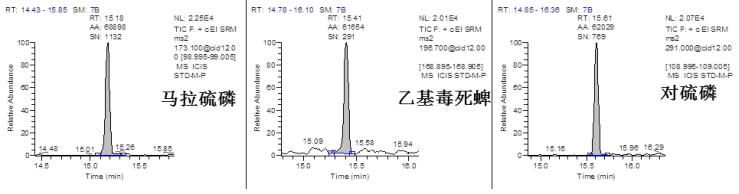
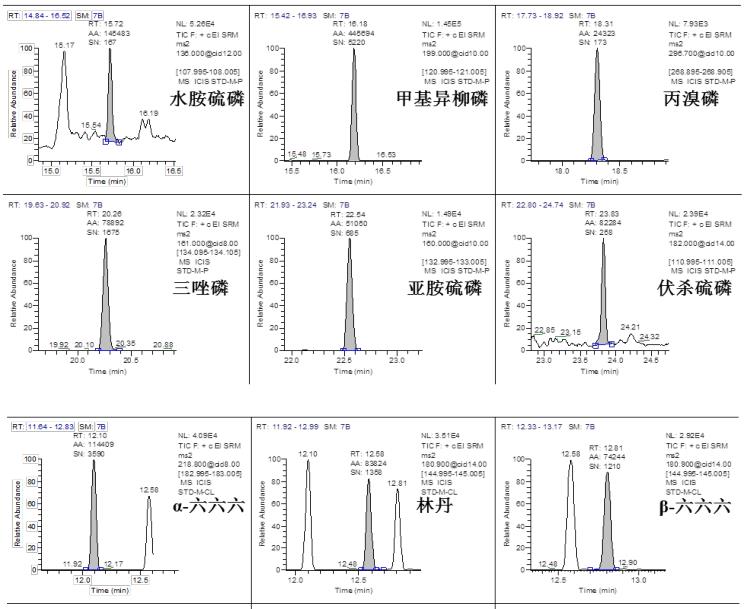
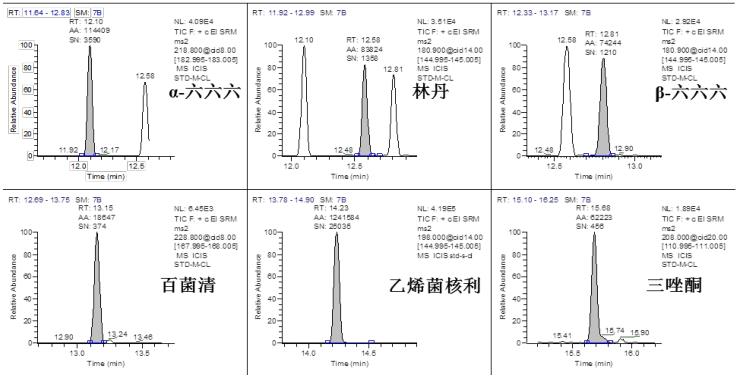
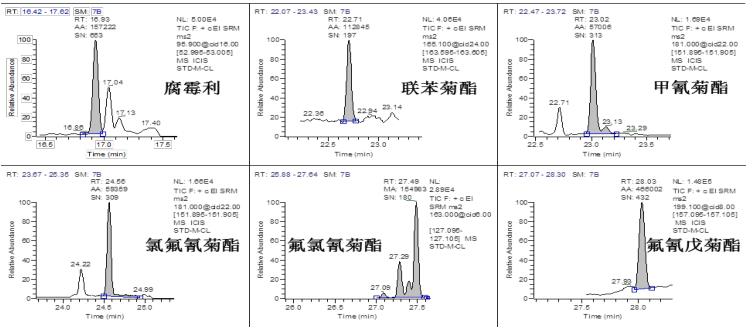
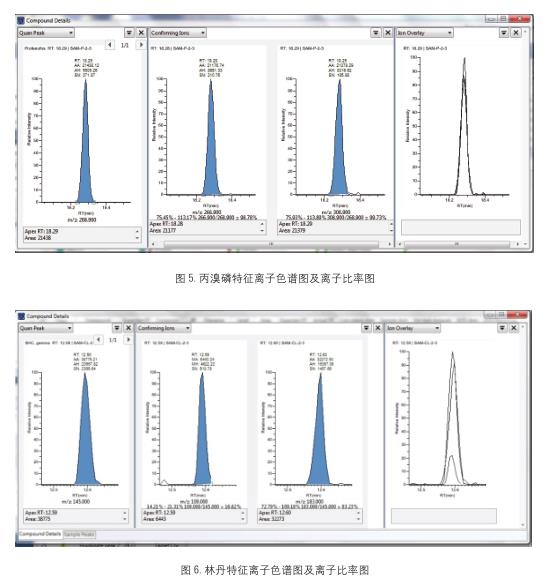
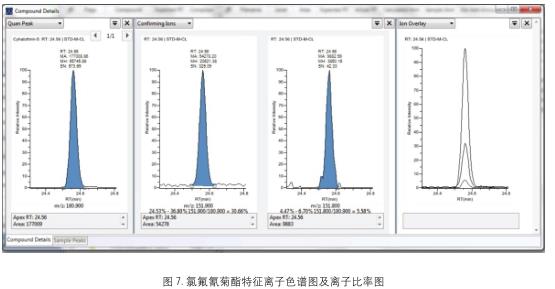
Qualitative results <br>According to the EU method directive [5], the confirmation requirements of the mass spectrometry method must reach four qualitative points. Tables 2 and 3 list the qualitative requirements of the specific judgment standards and common detection methods. For GC-MS/MS, there are 5-6 qualitative points for 3 pairs of ion pairs , which fully meet the requirements of the relevant methods. Therefore, a good qualitative effect is achieved. Figure 5, Figure 6, and Figure 7 show the characteristic ion chromatograms and ion ratios of the pesticides profenofos, lindane and cyhalothrin in the samples. 
Quantitative result
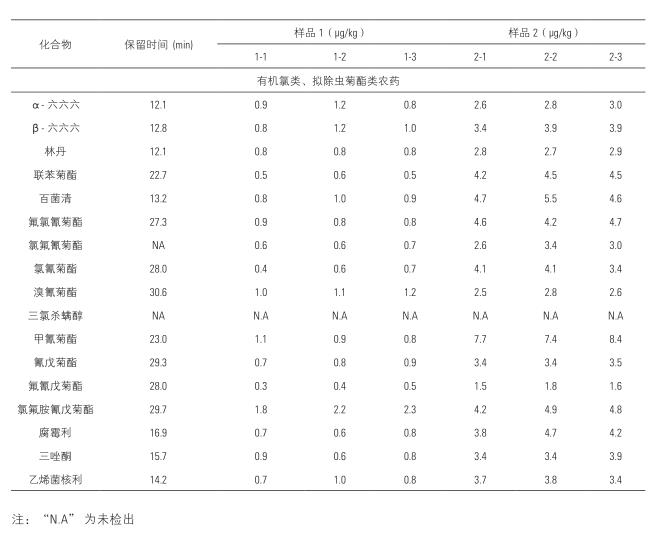
Trace Finder software accurately quantifies the pesticide residues contained in a sample while determining the type of pesticide. A standard curve was established using matrix standards to quantify pesticide residues in the samples. The results showed that, for the quantitative level of a particular compound of the instrument reaches 1 μg / kg or less, fully meet the requirements of daily pesticide residue detection (10 μg / kg), and at low concentrations can be obtained excellent effects and stable repetition spectra Sex. The pesticide concentrations of each target detected in the actual samples are shown in Table 4. 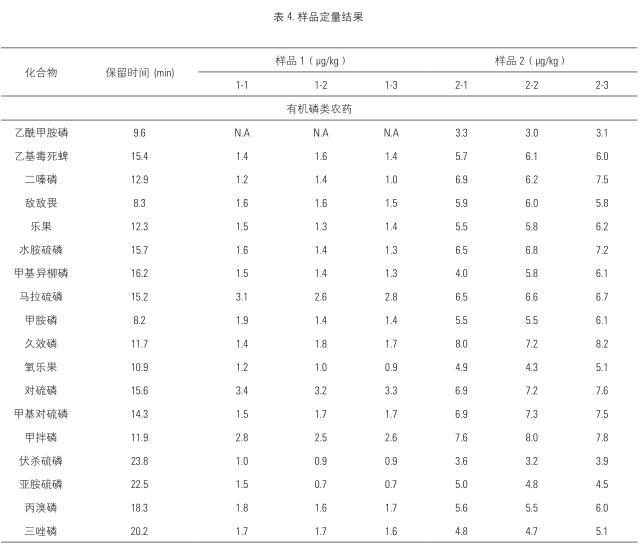
Instrument Stability Test <br>The two matrix standard samples were injected continuously for 10 times, and the relative standard deviation (RSD) of each target concentration was calculated. The stability of the test instrument is shown in Fig. 8. The results showed that all pesticide compounds had RSD below 20%. 35 pesticide compounds RSD < 15%, accounting for 91.4% of the total. The results of continuous injection of the instrument at low concentration levels (≤ 10 μg/kg) show that the instrument is stable and meets the testing requirements. 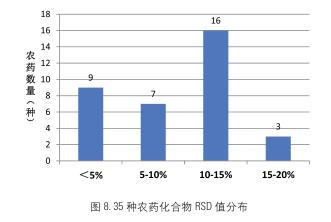
The Thermo Fisher Pesticide Screening Method contains information on 670 pesticide compounds. The compounds involved in the method package are common pesticide residues. The screening method is fast, simple, and reliable. The experimental results show that TSQ8000 Evo has high selectivity, high sensitivity, high stability and high throughput in the qualitative and quantitative application of pesticide residues in agricultural products. The qualitative and quantitative results are good, and it can fully meet the uncertain pesticides in the actual samples required by regulatory authorities. Low concentration screening, validation and quantitative analysis requirements.
[1] http: / /
[2] Li Xiaojuan et al. Characteristics of Chromatography-Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry and Its Application in Food Contaminant Analysis[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2012, 31(5): 628-632.
[3] Chen Yanqing, Yan Liushui. Progress in Pretreatment Technology of Pesticide Residues in Foods[J].Jiangxi Chemical Industry,2004(3):17-23.
[4] NY/T 761-2008 Determination of Organophosphorus, Organochlorine, Pyrethroid and Carbamate Pesticide Residues in Vegetables and Fruits
[5] European Union (2002) commission decision 2002/657/EC of 12 August 2002 implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC concerning the performance of analytical methods and the interpretation of results.