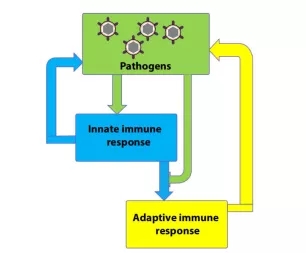
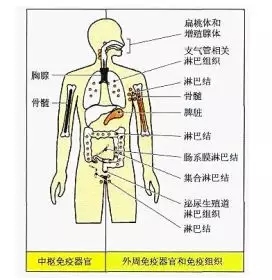
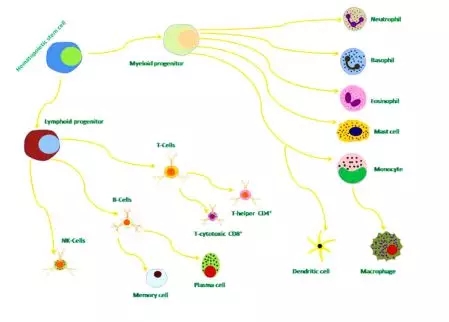
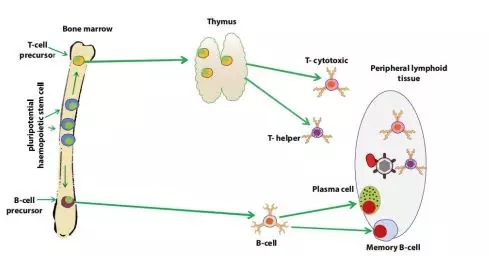
Winter is here, at this moment, Xiaobian wants to swear poetry, cough and cough... can't run the problem, the matter is important... In the cold winter season, whether it is in the snowy Northland or the cold southern part of the country, how many small partners have already fallen under the "claw" of the flu? The "iron man" who are still eating and fragrant, as strong as a cow, only sigh their own "firewall" - why the immune system is so weak, even a small bacterial virus can do it! In fact, the body's immune system is always fighting the "marathon" of the source of the disease to prevent its harm to the human body. Millions of immune cells are produced every minute: T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes, NK cells (natural killer cells), and phagocytic cells. They always have to produce a variety of immune factors and secrete a large number of antibodies against the enemy inside and outside the body! In normal people, immunity is the defense against human disease, but for people with cancer, the level of immunity determines the length of life of cancer patients [2] . Next, please follow the pace of the small devil, and explore the mystery of the "immune system" together! ! ! Figure 2. Image from the network [3] The immune system is a defense system of our body, "stationing and whistling" for our physical health. It is mainly composed of immune organs, immune cells and immune molecules. It has a pair of powerful "eyes", not only can find bacteria, fungi, parasites and other pathogens in the complex structure of the body, but also give them a "head-on attack", so that their plans to harm the body can not succeed. Figure 3. Schematic diagram of the immune system classification [4] The family of the immune system consists of two brothers: "free big" and "free two" [5] . The name "free big" is called the innate immune system . It was born with people. In short , it is a physical barrier built through the skin and mucous membranes to prevent pathogen invasion . This is the body's first line of defense. Such a "copper wall barrier" blocks many pathogens out of the body. Of course, pathogens will not eat "closed doors" forever, and in the fight against the immune system, there will be even more powerful roles. The immune system naturally does not sit still, and in the process of being attacked, another powerful army is established. They can not only identify the enemy's identity, but also "prescribe the right medicine" to defend the health of the body. This is "free of two." The name is called the acquired immune system and can be activated by an innate immune response. In this layer of defense, the immune system improves the identification of pathogens through an adaptive immune response during infection. After the pathogen is cleared, this adaptive immune response is still preserved in an "immune memory"; when the pathogen is reinfected, the adaptive immune system uses "memory" to make it faster and stronger. Immune attack [6] . Figure 4. The innate immune response can be directly activated by pathogens to resist persistent infection by microorganisms. The activated innate immune response can further trigger the body's acquired immune response, thereby killing the pathogen [7] Immune organs are organs and tissues that can achieve immune function , and are places where immune cells occur, settle, and exert effects . According to different functions, it can be divided into central immune organs and peripheral immune organs. Central immune organs and tissues are places where immune cells are produced, differentiated, developed, and matured, including bone marrow and thymus ; peripheral immune organs and tissues are places where immune cells settle, and are places where immune cells exert immune response effects, including spleen, lymph nodes, and Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue . Figure 5. Distribution of immune organs [8] An immune cell is a cell involved in or associated with an immune response process. Including lymphocytes, antigen presenting cells, granulocytes, and the like. All cells of the immune system are bone marrow-derived white blood cells (myeloid and lymphoid leukocytes) that function differently (Figure 6). Figure 6. Origin of the immune system cells [9] The main mediators of adaptive immunity are lymphocytes : B lymphocytes mediate immune responses by secreting antibody-mediated mediators; whereas T lymphocytes mediate cellular immune responses. The names of B cells and T cells are derived from the organs in which they develop: B cells develop in the bone marrow; T cells develop in the thymus. Despite the different origins, both B cells and T cells were derived from the same pluripotent bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells (Fig. 7). Figure 7. Bone marrow (the main site of B cell development) and thymus (the site of T cell development) are called central lymphoid organs, because lymphocytes are developed from T and B precursor cells produced in the bone marrow. The precursor cells are all produced by hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow. Mature lymphocytes can respond to antigens in peripheral lymphoid tissues (such as lymph nodes or spleen) where they continue to differentiate and become activated cells [9] Immune molecules are products secreted by immune cells, including antibodies (immunoglobulins), complements, cytokines, and the like. First, it is distinguished by structure and classification , including cytokines, chemokines and their receptors; complement and its regulatory molecules; differentiation antigen; adhesion molecules; TCR, BCR and antibody molecules; MHC gene products. Secondly, it is functionally distinguished , including molecules involved in the development and differentiation of immune cells; molecules involved in the inflammatory response and innate immune response; molecules involved in antigen recognition and exerting synergistic stimulation and inhibition; involved in the activation and suppression of immune cells Molecules; molecules involved in immune cell apoptosis and causing cell lysis. Introduction to the immune system, Xiaobian only said so much for the time being (content is too complicated, Rong Xiaobian slowly.....) Finally attached to the immune-related healthy life tips , I hope that your friends can eat well Good sleep, good exercise, and soon have the body of "hundred poisons" Figure 8. Tips for healthy living [13] 1) There is also a close relationship between the immune system and sleep and rest [10] Sleeping is an instinctive physiological response of the human body. It is the result of inhibition after the nerve cells in the cerebral cortex continue to excite. When the inhibition is dominant in the cerebral cortex, people sleep. The inhibition is to protect the nerve cells so that it can re-energize and let people continue to work. If lack of sleep leads to a decrease in immunity, the number of "killer cells" that are resistant to germs is reduced. Studies have shown that people who sleep only 4 hours a night have 50% less antibodies to the flu in the blood than those who sleep 7-8 hours a night! So Xiaobian suggested that everyone should keep a good sleep every day~ 2) The function of the immune system depends on normal nutrient supply For a long time, people have reached a consensus that severe malnutrition can lead to immunodeficiency. Similarly, diseases caused by overnutrition, such as diabetes and obesity, can destroy immune function. Moderate malnutrition and the lack of specific trace elements and nutrients also reduce the immune response [11] . 3) Food can affect the immune system Fresh fruits, vegetables and foods rich in specific fatty acids can help maintain a healthy immune system [12] . Healthy eating plays a vital role in strengthening the body's resistance, so you can eat more nutritious vegetables and fruits. These foods not only contain vitamins, but also many phytochemicals that are very beneficial to health. Hula Hula... Today’s Science and Technology Xiaobian introduces this first. If the content of the article is in the heart of everyone, don’t worry, keep an eye on the “Princess†of the 100 Olympics, let us look forward to the next meeting. Refill ing~ Reference materials: 1.http://m.sohu.com/a/203777221_349270 2.http://sh.qihoo.com/pc/9d796a1b9728d3991?sign=360_e39369d1 3.http://17qq.com/biaoqing/1883967_p5.html 4.https:// 5.https:// 6. Mayer, Gene. Immunology - Chapter One: Innate (non-specific) Immunity. Microbiology and Immunology On-Line Textbook. USC School of Medicine. 2006[1 January 2007]. 7. Scully, Georgakopoulou EA, Hassona Y. The Immune System: Basis of so much Health and Disease: 3. Adaptive Immunity. Dent Update. 2017 Apr; 44(4): 322-4, 327 8.https://tse3.mm.bing.net/th?id=OIP.sDSHgwX4AOUrt-9qori9TwAAAA&pid=Api 9. Scully, Georgakopoulou EA, Hassona Y. The Immune System: Basis of so much Health and Disease: 1. Overview of Immunity and the Immune SystemDent. Update 2017; 44: 151–156 10. Lange T, Perras B, Fehm HL, Born J. Sleep enhances the human antibody response to hepatitis A vaccination. Psychosomatic Medicine. 2003, 65(5): 831–5. 11.RM Suskind, CL Lachney, JN Udall, Jr., "Malnutrition and the Immune Response", in: Dairy products in human health and nutrition, M. Serrano-RÃos, ed., CRC Press, 1994. 12.Pond CM. Adipose tissue and the immune system. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes, and Essential Fatty Acids. July 2005, 73(1): 17-30 13.https://=.html Wenzhou Celecare Medical Instruments Co.,Ltd , https://www.celecaremed.com
Figure 1. Improve immunity and easily resist viral invasion [1] 

~


Scan code to pay attention to the 100 Olympics map to learn more about consulting
Immune organ
Immune Cells
Immune molecule